Chapter 1.5
DEFINITIONS
Sections:
1.5.100 Purpose.
The purpose of this chapter is to define terms that are used frequently in the city of Silverton development code, to assist decision makers in interpreting and applying the code. Some of the terms that are defined here may have different meanings in other communities. (Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)
1.5.200 Applicability.
A. Definitions. The definitions in this chapter apply to all actions and interpretations under the city of Silverton development code. The meanings given terms in this chapter may, in certain contexts in which they are used, be clearly inapplicable. In such cases the context in which a term is used will indicate its intended meaning, and that intent shall control. Where a term used in this code is already defined in another part of the city of Silverton code (e.g., the International Building Code, etc.) the term is not redefined herein for purposes of that other code.
B. Land Use Categories. Chapter 1.6 SDC provides descriptions of the land use categories used in Article 2.
C. Interpretation. Terms not defined in this code shall have their ordinary accepted meanings within the context in which they are used. Webster’s Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged, shall be considered a standard reference. In some situations, the community development director may find it necessary to make a formal code interpretation or similar use ruling under Chapter 4.8 SDC. In such cases, the director’s decision shall be processed through either a Type I or Type II procedure and a written record of it shall be kept on file with the development code. (Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)
1.5.300 Definitions.
The following definitions are organized alphabetically and some related terms are also grouped together and cross-referenced under group headings (e.g., Transportation-Related, Environment-Related, etc.). See also Chapter 1.6 SDC for descriptions of the land use categories used in Article 2.
A. “A” Definitions.
“Abutting” means contiguous or adjoining. It shall include the terms “adjacent,” “adjoining” and “contiguous.”
“Access” means a way or means of approach to provide pedestrian, bicycle, and/or motor vehicular entrances or exits to a property.
“Accessory” means secondary or incidental to a primary use or structure.
Accessory Dwelling Unit. See Residential Structure Types.
“Accessory parking facility” means a parking facility that provides parking for a specific use or uses. The facility may be located on or off the site of the use or uses to which it is accessory. A fee may or may not be charged. An accessory parking facility need not be in the same ownership as the specific uses to which it is accessory. See also commercial parking in Chapter 1.6 SDC, Use Categories.
“Accessory structure” means a structure of secondary importance or function on a site. In general, the primary use of the site is not carried on in an accessory structure. Accessory structures are detached from the primary structure. Examples of accessory structures include but are not limited to: garages, decks, fences, arbors, gazebos, heat pumps, and other structures. See also “Primary structure.”
“Accessory use” means a use or activity that is a subordinate part of a primary use and that is clearly incidental to a primary use on a site. Does not include an accessory dwelling. See also “Primary structure.”
“Adjacent” means abutting or located directly across a street right-of-way.
“Adjustment” means a discretionary approval that modifies or waives a specific development standard, as expressly allowed under this code (e.g., SDC 4.2.510, Design review – Adjustments (performance option)).
“Administrative” means a discretionary action or permit decision made without a public hearing, but requiring public notification and an opportunity for appeal.
“Adult foster care” means a family home or facility in which residential care is provided for five or fewer adults who are not related to the provider by blood or marriage. “Provider” means any person operating an adult foster care home. See also “Group living structure” under Residential Structure Types.
“Adverse impact or effect” means negative effect that can be measured (e.g., noise, air pollution, vibration, dust, glare, emissions, etc.).
“Affordable” means housing affordable to a certain percentage of the population earning a specified level of income and spending no more than 30 percent of their income on housing expenses. For more information, contact the federal Department of Housing and Urban Development and the Oregon Department of Housing and Community Services.
“Aged person” means an individual 65 years of age or older.
Agriculture. See use category under Chapter 1.6 SDC and ORS 215.203(2)(a).
Alley. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Alteration. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Ambient” means the normal or background environmental condition, as in the level of light, dust or noise.
“Applicant” means a person who applies for a land use review or building permit. An applicant can be the owner of the property or someone who is representing the owner, such as a builder, developer, optional purchaser, consultant, or architect.
“Arborist” means a professional listed as a certified arborist or a registered consulting arborist.
Arterial. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
“Articulate/articulation” means the joining and interrelating of building spaces through offsets, projections, overhangs, extensions and similar features.
Attached House (Townhome or Rowhouse). See Residential Structure Types.
Attached Structure. See Development-Related Definitions.
Automobile-Dependent/Oriented Development. See Development-Related Definitions.
B. “B” Definitions.
“Basement” means a portion of a building, not deemed a story, where the floor level directly above is six feet or less above grade for more than 50 percent of the total perimeter and is less than 10 feet above grade at every point.
“Bed and breakfast inn” means any establishment located in a structure designed for a single-family residence and structures appurtenant thereto that:
1. Has rooms for rent on a daily basis to the public;
2. Offers a breakfast meal as part of the cost of the room; and
3. Is developed in accordance with SDC 2.2.200.
“Berm” means a small rise or hill in a landscape that is intended to buffer or visually screen certain developments, such as parking areas.
“Block” means all of the property bounded by streets, rights-of-way, and water features, but not divided or separated in any way by streets or water features.
“Block frontage” means all of the property fronting on one side of a street that is between intersecting or intercepting streets, or that is between a street and a water feature or end of a dead-end street. An intercepting street determines the boundary of the block frontage only on the side of the street that it intercepts. See Figure.
Block Frontage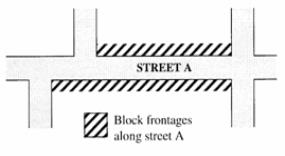
“Bollard” means a permanent or removable post of metal, wood or masonry that is used to separate or direct traffic (vehicles, pedestrians and/or bicycles); may contain sidewalk or pathway lighting.
Boulevard. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
“Building” means a structure that has a roof and is enclosed on at least 50 percent of the area of its sides. See Development-Related Definitions for related definitions.
“Building official” means the person who enforces the building ordinances and regulations for the city, and other ordinances and regulations as assigned.
Build-to Line. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Business street” means any block length along any street, other than an arterial, within which there is or will be provided access to one or more commercial structures which in the judgment of the planning commission will result in a high volume of business traffic on such street.
C. “C” Definitions.
“Canopy” means a permanent roofed structure that may be free-standing or be partially attached to a building, for the purpose of providing shelter to patrons on foot and/or in motor vehicles; does not include a completely enclosed structure. See also “Tree canopy” under Environment-Related Definitions.
“Capacity” means maximum holding or serviceability, as used for transportation, utilities, parks and other public facilities.
“Carport” means a stationary structure consisting of a roof, its supports, and not more than one wall or storage cabinets substituting for a wall, used to shelter motor vehicles, recreational vehicles, or boats.
“Centerline radius” means the radius of a centerline of a street right-of-way.
“Certificate of occupancy” means a certificate of occupancy or a certificate of inspection issued by the city at the completion of a building permit or change of occupancy.
“Change in occupancy” means a change in the use of a structure that results in a different classification as defined by this code or the International Building Code.
“Change of use” means a change in the primary type of use on a site.
Child Care Center, Family Child Care. See use categories, SDC 1.6.430 and 1.6.440.
“City” means the city of Silverton, Oregon.
“Clear and objective” means decision criteria and standards that do not involve substantial discretion or individual judgment in their application.
“Clear zone” means the ground area under the approach surface which extends from the end of the runway to a point where the approach surface is 50 feet above the runway in elevation.
Clearing. See Development-Related Definitions.
Collector. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
“Commercial” means land use involving buying/selling of goods or services as the primary activity.
“Common area” means land commonly owned, to include open space, landscaping or recreation facilities (e.g., typically owned by a homeowners’ association).
“Comprehensive plan” means the current adopted comprehensive plan of the city of Silverton.
“Conditional use” means a use that requires a conditional use review. See Chapter 4.4 SDC.
Condominium. See Residential Structure Types.
Conservation Easement. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Corner Lot. See “Lot, Corner lot.”
“Corner radius” means the radius of a street corner, as measured around the curb or edge of pavement.
Cottage. See Residential Structure Types.
“Council” means the city council of Silverton, Oregon.
Courtyard. See Development-Related Definitions.
Crown Cover. See Environment-Related Definitions.
D. “D” Definitions.
“Days” means calendar days, unless specifically stated as working days. Working days include Monday through Friday, excluding holidays.
Dead-End Street. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
“Dedication” means the designation of land by its owner for any public use as shown on a subdivision plat or deed. The term may also be used for dedications to a private homeowners’ association.
“Density(ies)” means a measurement of the number of dwelling units in relationship to a specified amount of land. As used in this code, density is determined based on the gross parcel or lot area, which includes land that will be dedicated as right-of-way through the development process. It does not include land previously dedicated as right-of-way. Density is a measurement used generally for residential uses.
“Design review” means a development review that addresses site and building design requirements of the applicable land use district and the design standards and public improvement requirements of this code. See Chapter 4.2 SDC.
Development-Related Definitions.
• “Alteration” means a physical change to a structure or site. Alteration does not include normal maintenance and repair or total demolition. (See also “Interior/exterior alteration.”) Alteration does include the following:
- Changes to the exterior of a building;
- Changes to the interior of a building;
- Increases or decreases in floor area of a building;
- Changes to other structures on the site, or the development of new structures;
- Changes to exterior improvements;
- Changes to landscaping; and
- Changes in the topography of the site.
• “Arcade” means an arched or covered passageway, e.g., along building fronts or between streets.
• “Attached structure” means any structure that is attached to another structure by a common wall, by a roof, or by structural connections that allow pedestrian access to both structures. For example, decks or stairways are attached structures when they are connected to another structure. A garage may be attached to another structure by sharing a wall or by a breezeway. Structures connected by an “I” beam or similar connections are not considered attached.
• “Automobile-dependent development” means primary or accessory uses servicing motor vehicles, or patrons in motor vehicles, such as motor vehicle repair, gas stations, car washes, auto and truck sales, drive-up windows, kiosks, and similar uses.
• “Automobile-oriented development” means development in which the site layout and design gives preference to automobiles as the primary mode of transportation; generally discouraged in all residential areas and most commercial and light industrial areas.
• “Building” means a structure that has a roof and is enclosed on at least 50 percent of the area of its sides.
• “Building area” means the total area of a building, both above and below ground, measured from the exterior faces of a building or structure. Gross building area does not include the following:
- Roof area;
- Rooftop mechanical equipment; and
- Roofed porches, exterior balconies, or other similar areas, unless they are enclosed by walls that are more than 42 inches in height, for 50 percent or more of their perimeter.
• “Building coverage” means the area that is covered by buildings, and decks, stairways and entry bridges that are more than 30 inches above grade. Eaves are not included in building coverage. Building coverage is included within lot coverage. See also “Lot coverage.”
• “Building envelope” means area outside of all required setbacks, easements or other constraints on a lot, which could accommodate a structure(s).
• “Building footprint” means the outline of a building, as measured around its foundation, or building coverage, whichever is greater.
• “Building height” means the vertical distance from the grade plane to the average height of a gabled roof, or the top of a mansard or flat roof including the parapet walls.
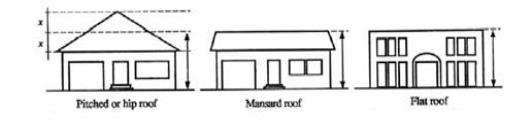
• “Building height step-down” means a development standard that requires a transition in allowable building height, whereby the buildings in a specific land use district must “step-down” in elevation where they abut a lower-intensity land use district.
• “Building line” means a line running parallel to a lot line that is the same distance from the lot line as the closest portion of a building on the site. See Figure.
Building Lines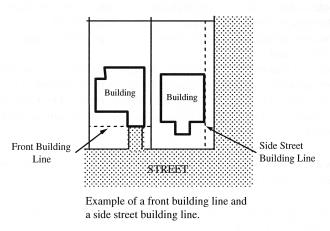
• “Building mass” means the aggregate size of a building, or the total height, width, and depth of all its parts.
• “Building pad” means a vacant building site on a lot with other building sites.
• “Building scale” means the dimensional relationship of a building and its component parts to other buildings.
• “Build-to line” means a maximum distance, or range within which, a building must be set back from a street right-of-way for pedestrian-orientation and human-scale design.
• “Clearing” means any activity that removes existing vegetation or strips surface material from any portion of the site.
• “Cornice” means the projecting horizontal element that tops a wall or flat roof.
• “Courtyard” means a court or enclosure adjacent to a building, which usually provides amenities such as gardens, planters, seating, or art.
• “Develop” means to construct or alter a structure or to make a physical change to the land including excavations and fills.
• “Development” means all improvements on a site, including buildings, other structures, parking and loading areas, landscaping, paved or graveled areas, and areas devoted to exterior display, storage, or activities. Development includes improved open areas such as plazas and walkways, but does not include natural geologic forms or unimproved land. See also “Exterior improvements.”
• Driveway. There are two types of driveways:
a. The area that provides vehicular access to a site from a street. A driveway is the same width as the curb cut excluding any aprons or extensions of the curb cut. This type of driveway begins at the street and extends into the site. A driveway does not include parking, maneuvering, or circulation areas in parking areas, such as aisles; and
b. The area that provides vehicular circulation between two or more noncontiguous parking areas. A driveway does not include maneuvering or circulation areas within the interior of a parking area. Where required by this code for fire safety, a driveway must be used exclusively for circulation, with no abutting parking spaces.
• “Driveway apron/approach” means the edge of a driveway where it abuts a public way; usually constructed of concrete.
• “Eave” means a projecting overhang at the lower border of a roof extending from a primary wall or support. See Figure.
Eave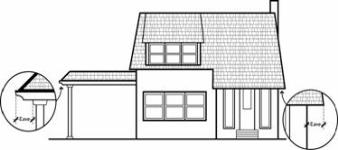
• “Exterior alteration” means an alteration that is outside any buildings.
• “Exterior improvements” means all improvements except buildings or other roofed structures. Exterior improvements include surface parking and loading areas, paved and graveled areas, and areas devoted to exterior display, storage, or activities. It includes improved open areas such as plazas and walkways, but does not include vegetative landscaping, natural geologic forms, or unimproved land. See also “Development.”
• “Facade” means the front or street-facing elevation of a structure.
• “Fire apparatus lane” or “fire lane” means a road or other way developed to allow the passage of fire apparatus. A fire lane is not necessarily intended for vehicular traffic other than fire apparatus.
• “Fire code” means the State of Oregon 2007 Fire Code Amendments, based on the International Fire Code, 2006 Edition, or as amended by the city of Silverton.
• “Floor area” means the total floor area of a building, both above and below ground, with a clear ceiling height of at least seven feet. Floor area is measured from the interior walls of a building or structure and does not include the following:
- Roof area;
- Rooftop mechanical equipment; and
- Roofed porches, exterior balconies, or other similar areas, unless they are enclosed by walls that are more than 42 inches in height, for 50 percent or more of their perimeter.
• “Foundation plane” means the surface area defined by a structure’s foundation, including the perimeter of all footings, slabs and pads.
• “Grading” means all cuts, fills, embankments, stockpile areas, and equipment maneuvering areas associated with development.
• “Impervious surface” means surface area that does not allow for water infiltration or has a runoff coefficient of 0.90 or more (i.e., nonpermeable pavement, solid rock, roofs, foundations, underground tanks and vaults, and similar areas). Gravel is deemed an impervious surface unless the city engineer finds otherwise.
• “New development” means development of a site that was previously unimproved or that has had previously existing buildings demolished; e.g., not a remodel of an existing building.
• “Paved area” means an uncovered, hard-surfaced area or an area covered with a perforated hard surface (such as porous concrete or pavers) that is able to withstand vehicular traffic or other heavy-impact uses. Graveled areas are not paved areas but are typically impervious.
• “Pedestrian amenity(ies)” means areas and objects that serve as places for public socializing and enjoyment and are usually closed to motorized vehicles. Examples include plazas, building frontage areas (extra-wide sidewalks), street furnishings (e.g., benches, drinking fountains, bus waiting shelters), and pocket parks adjacent to a street, and similar areas and objects. Sidewalks designed to meet the minimum sidewalk width standards under Chapter 3.4 SDC are not “amenities” for the purpose of this code.
• “Pedestrian-oriented development” means development that is designed with an emphasis primarily on the street sidewalk and on pedestrian access to the site and building, rather than on auto access and parking areas. The building is generally placed close to the street and the main entrance is oriented to the street sidewalk. There are generally windows or display cases along building facades which face the street. Typically, buildings cover a large portion of the site. Although parking areas may be provided, they are generally limited in size and they are not emphasized by the design of the site.
• “Ridgeline (building)” means the top of a roof at its highest elevation.
• “Roof pitch” means the slope of a roof, usually described as a ratio (e.g., one foot of rise per two feet of horizontal distance equals 6:12 roof pitch).
• “Shared driveway” means when land uses on two or more lots or parcels share one driveway. An easement or tract (owned in common) must be created and recorded for this purpose.
• “Shared parking” means required parking facilities for two or more uses, structures, lots or parcels, which are satisfied jointly with the same facilities. See Chapter 3.3 SDC.
• “Shopping street” means a driveway in a commercial development that is designed to mimic a public street with sidewalks, tree wells, pedestrian lighting, and street furnishings. A shopping street may also have on-street parking.
• “Storefront character” means the character expressed by buildings placed close to the street with ground-floor display windows, weather protection (e.g., awnings or canopies), corner building entrances or recessed entries, and similar features.
• “Stormwater facility” means a facility designed to improve the quality and manage the quantity of stormwater runoff. Stormwater facilities include vegetated swales and sand filters, wet or dry ponds, marshes, infiltration facilities, and structural storm sewer devices. Stormwater facilities do not include conveyance systems that are meant only for conveying the stormwater from one place to another and do not affect the quality or quantity of the stormwater.
• “Street-facing facade/wall” means all the wall planes of a structure as seen from one side or view that are at an angle of 45 degrees or less from a street lot line. See Figure.
Street-Facing Facade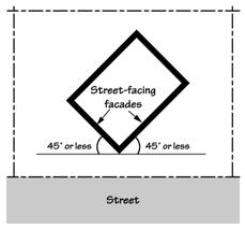
• “Street furniture/furnishings” means benches, lighting, bicycle racks, drinking fountains, mailboxes, kiosks, and similar pedestrian amenities; may be located within a street furnishings zone or building front zone of a sidewalk or in a plaza. See also “Pedestrian amenity(ies).”
• “Structure” means any object constructed in or on the ground. “Structure” includes buildings, decks, fences, towers, flagpoles, signs, and other similar objects. “Structure” does not include paved areas or vegetative landscaping materials.
• “Structure height” means the height of a structure, and the cumulative height of a building with any appurtenant structures.
• “Swale” means a type of stormwater facility, usually a broad, shallow depression with plants that filter and process contaminants.
• “Vehicle areas” means all of the areas on a site where vehicles may circulate or park including parking areas, driveways, drive-through lanes, and loading areas. See also “Driveway” and “Parking area.”
“Development review” is a generic term meaning any type of review undertaken to ensure compliance with this code.
Disabled Person. For the purposes of this code, a “disabled person” is a person who has a condition of physical or mental disability that substantially limits one or more major life activities as stated in Section 504 of the Federal Rehabilitation Act of 1973 and state law.
“Discontinued use” means a use that physically left the land it was on, a permitted use that ceased, or a use terminated at the end of a lease or contract. See Chapter 5.2 SDC, Nonconforming Uses and Developments. A use is considered temporarily discontinued during the first year after it ceases, after which it is considered permanently discontinued.
“Discretionary” means a permit action or decision that involves substantial judgment or discretion.
Disturbance Area. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Drainage Way. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Drip-Line. See Environment-Related Definitions.
“Drive-through/drive-up facility” means a facility or structure that is designed to allow drivers to remain in their vehicles before and during an activity on the site. Drive-through facilities are a type of site development that is usually found in conjunction with a quick vehicle servicing use or a retail sales and service use. Drive-through/drive-up facilities also include facilities designed for the rapid servicing of vehicles, where the drivers may or may not remain in their vehicles, but where the drivers usually either perform the service for themselves or wait on the site for the service to be rendered. Drive-through facilities may serve the primary use of the site or may serve accessory uses. Examples are drive-up windows; automatic teller machines; coffee kiosks and similar vendors; menu boards; order boards or boxes; gas pump islands; car wash facilities; auto service facilities, such as air compressor, water, and windshield washing stations; quick-lube or quick-oil change facilities; and drive-in theaters.
Driveway. See Development-Related Definitions for examples and related definitions.
“Drought-tolerant/drought-resistant plants” or “xeriscaping” means as listed and described in the Sunset Western Garden Book (latest edition) or similar authoritative regional resource approved by the city.
Duplex. See Residential Structure Types.
“Dwelling unit” means a building, or a portion of a building, that has independent living facilities including provisions for sleeping, cooking, and sanitation, and that is designed for residential occupancy by a group of people. Buildings with more than one set of cooking facilities are considered to contain multiple dwelling units or accessory dwelling units, unless the additional cooking facilities are clearly accessory to the primary use, such as an outdoor grill. See also Residential Structure Types for examples and related definitions.
E. “E” Definitions.
“Easement” means a grant of rights by a property owner that allows others to use the owner’s land for a specific purpose, such as access, or to locate utilities. Recorded and on record at Marion County.
Eave. See Development-Related Definitions for illustration and related definitions.
“Elevation” means a scaled drawing of the outside wall of a building or structure, from grade to roof ridgeline, typically specifying materials, color, and dimensions.
“Emergency” means any event or circumstances posing an imminent threat to person or property, or including but not limited to: fire, explosion, flood, wind, landslide, severe weather, drought, earthquake, volcanic activity, improper storage, stockpiling, spill, or release of flammable or hazardous materials, contamination, utility or transportation emergencies, disease, blight, and civil disturbance.
Environment-Related Definitions.
• “Conservation easement” means an easement that protects identified conservation values of the land, such as wetlands, woodlands, significant trees or groves, floodplains, wildlife habitat, and similar resources, typically in perpetuity.
• “Crown cover” means the area directly beneath the crown and within the drip-line of a tree or shrub. The crown consists of the aboveground branches, stems, and leaves.
• “Detention facility (stormwater)” means the temporary storage of stormwater (i.e., as in a stormwater detention facility) before it is released through an engineered system that is designed to slow runoff. Detention facilities may be designed to filter or biologically process stormwater runoff, improving water quality before it is released. See also “Retention facility (stormwater).”
• “Disturbance area” means an area that contains all temporary and permanent development, exterior improvements, and staging and storage areas on the site, both existing and proposed. Vegetation planted for resource enhancement and agricultural and pasture land is not included.
• “Drainage land” means land required for drainage ditches or required along a natural stream or watercourse for preserving the channel and providing for the flow of water therein to safeguard the public against flood damage or the accumulation of surface water.
• “Drainage way” means an open linear depression, whether constructed or natural, that functions for the collection and drainage of surface water. It may be permanently or temporarily inundated.
• “Drip-line” means an imaginary line around a tree or shrub at a distance from the trunk equivalent to the canopy (leaf and branch) spread.
• “Ecologically/scientifically significant natural areas” means land and water that has substantially retained its natural character, but is not necessarily completely natural or undisturbed, and which is significant for historical, scientific, paleontological, archeological, or natural features.
• “Fish and wildlife habitat areas” means lands that contain significant food, water, or cover for native terrestrial and aquatic species of animals. Examples include forests, fields, riparian areas, wetlands, and water bodies.
• “Flood” or “flooding,” as designated by the National Flood Insurance Act of 1968, means the general and temporary condition of partial or complete inundation of normally dry land areas from:
- The overflow of streams, rivers or other inland water.
- The unusual and rapid accumulation or runoff of surface waters from any source.
- Mudslides (i.e., mudflows).
- “Flooding” also means the collapse or subsidence of land along a water body as a result of erosion or undermining exceeding anticipated levels or suddenly caused by an unusually high water level.
• “Flood elevation determination” means a determination by the Federal Insurance Administrator of the water surface elevations of the base flood from the best available data source.
• “Flood hazard area” means areas subject to periodic water inundation, as identified on the flood insurance rate map for Marion County and its incorporated communities.
• Flood Hazard Map. The official map of Silverton is the flood insurance rate map (FIRM) for Marion County and incorporated communities. The FIRM delineates a special flood hazard area or floodplain where regulations apply.
• “Floodplain” is a physical geographic term describing any land area susceptible to being inundated by water from any source.
• “Floodplain management” means the operation of an overall program of corrective and preventative measures for reducing flood damage, including but not limited to emergency preparedness plans, flood control works and floodplain management regulations.
• “Floodproofing” means any combination of structural and nonstructural additions, changes or adjustments to structures that reduce or eliminate flood damage to real property, water and sanitary facilities, structures, and their contents.
• “Floodway, regulatory” means the channel of a river or other watercourse and the adjacent land areas that must be reserved in order to discharge the waters of a base flood without cumulatively increasing the water surface elevation.
• “Identified natural features (e.g., wetlands or streams)” means natural features that are identified in the National Wetlands Inventory, and/or other references used by the city or natural resource regulatory agency, as being significant and in need of protection.
• “Retention facility (stormwater)” means the infiltration of stormwater (i.e., as in a stormwater retention facility) in an engineered system that is designed to contain runoff on a development site. Retention facilities are typically designed to filter or biologically process stormwater runoff, improving water quality before it is released. See also “Detention facility (stormwater).”
• “Riparian areas” means lands adjacent to rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, and other water bodies. They are transitional between aquatic and upland zones, and as such, contain elements of both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They have high water tables because of their close proximity to aquatic systems, soils that are usually made up largely of water-carried sediments, and some vegetation that requires free (unbound) water or conditions that are more moist than normal.
• “Sensitive lands” means wetlands, significant vegetation, steep slopes, floodplains and other natural resource areas designated for protection or conservation by the development code, comprehensive plan, refinements to the comprehensive plan, or individual site inventory or study as may be required by the city, state or federal natural resource agency through the development review process.
• “Shoreline” means banks and other areas adjacent to a river, stream, creek, lake or similar water body.
• “Shoreline stabilization” means the protection of a shoreline by city-approved vegetative or structural means.
• “Stream” means an area where enough natural surface water flows to produce a stream channel, such as a river or creek that carries flowing surface water either intermittently or during most of the year. This includes:
- The water itself, including any vegetation, aquatic life, or habitat;
- Beds and banks below the high water level that may contain water, whether or not water is actually present;
- The floodplain between the high water levels of connected side channels;
- Beaver ponds, oxbows, and side channels if they are connected by surface flow to the stream during a portion of the year; and
- Stream-associated wetlands.
• “Stream channel” means an area with evidence of perennial or seasonal water passage. The depression between the banks worn by the regular and usual flow of the water. The channel need not contain water year-round. This definition does not include irrigation ditches, canals, storm or surface water runoff devices, or other entirely artificial watercourses.
• “Top of bank” means the first major change in the slope of the incline from the ordinary high water level of a water body. A “major change” is a change of 10 degrees or more. If there is no major change within a distance of 50 feet from the ordinary high water level, then the top of bank will be the elevation two feet above the ordinary high water level.
• “Tree canopy” means the ground area that, when viewed from above the crown of one or more trees, is mostly covered by the tree(s). For deciduous trees, canopy area is based on the time of year when foliage is present.
• “Water bodies” means permanently or temporarily flooded lands that may lie below the deepwater boundary of wetlands. Water bodies include rivers, streams, creeks, sloughs, drainage ways, lakes, and ponds.
• “Wetland” means an area that is inundated or saturated by surface or ground water at a frequency and duration sufficient to support, and that under normal circumstances does support, a prevalence of vegetation typically adapted for life in saturated soil conditions. Wetlands include swamps, marshes, bogs, and similar areas.
“Evidence” means application materials, plans, data, testimony and other factual information used to demonstrate compliance or noncompliance with a code standard or criterion.
“Excavating or filling” means the removal, placement, or replacement of earth, concrete, asphalt, and similar nondecomposable materials whether permanent or temporary in nature. “Excavating or filling” does not include the movement of earth or placement of gravel, asphalt, or other paving materials that is done in conjunction with road improvements. It does not include the excavation of mineral or aggregate resources. “Excavating or filling” includes the terms “grading,” “preloading,” “surcharging,” and “stockpiling.”
“Exterior display” includes the outdoor display of products, vehicles, equipment, and machinery for sale or lease. “Exterior display” is an outdoor showroom for customers to examine and compare products. There is variety or a distinction among the goods on display, through different products, brands, or models. The display area does not have to be visible to the street. “Exterior display” does not include goods that are being stored or parked outside, if there is no variety or distinction among the goods, and the goods are not examined and compared by customers. It does not include damaged or inoperable vehicles, vehicles or equipment being serviced, bulk goods and materials, and other similar products. “Exterior display” does not include car and boat sales and leasing when such vehicles are not accessible to customers to inspect and compare; this situation is considered exterior storage. Examples of uses that often have exterior display are car and boat sales and leasing, and plant nurseries. See also “Exterior work activities” and “Exterior storage.”
Exterior Improvements. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Exterior storage” means the outdoor storage of goods that generally have little or no differentiation by type or model. The goods may be for sale or lease, but if so, they are the type that customers generally do not inspect and compare. Exterior storage also includes the outdoor storage of goods for sale, lease or rent that may be differentiated by type or model, but that are not accessible for customers to inspect or compare. Exterior storage includes the storage of raw or finished goods (packaged or bulk), including gases, oil, chemicals and gravel; building materials and packing materials; salvage goods; machinery, tools, and equipment; vehicles that are for sale, lease or rent, which are not accessible to the customer to inspect or compare; vehicles that have been unloaded at port facilities and are waiting transport to off-site locations; vehicles that have been towed and are being kept in an impound lot; and other similar items. The storage of recreational vehicles outdoors is also considered exterior storage. Damaged or inoperable vehicles, or vehicles that have missing parts, which are kept outside are also included as exterior storage. Examples of uses that often have exterior storage are lumber yards, wrecking yards, tool and equipment rental, bark chip and gravel sales, car dealerships or car rental establishments, and port facilities. See also “Exterior display” and “Exterior work activities.”
“Exterior work activities” include the outdoor processing, assembly, or fabrication of goods; the maintenance, repair, and salvage of vehicles and equipment; and other similar activities that generally have an industrial orientation. “Exterior work activities” do not include normal pick-up and deliveries to a site, parking, excavation and fills, exterior eating areas, outdoor recreation, or outdoor markets. See also “Exterior display” and “Exterior storage.”
F. “F” Definitions.
“Facade” means the front or street-facing elevation of a structure. See Development-Related Definitions for related definitions.
Family Daycare. See Child Care Center, Family Child Care.
Farming or Farm Use. As used in this code, “agriculture” is the same as “farm use.” [See ORS 215.203(2)(a).] Includes utilization of land to raise, harvest, or sell crops; feed, breed, manage, and sell livestock, poultry, fur-bearing animals, honeybees, or their produce; dairies and selling dairy products; or any other agricultural or horticultural use, animal husbandry, timber agricultural use, or combination thereof. Farm uses include preparation or processing and storage of products raised on such land, but do not include construction or use of dwellings and other buildings customarily provided in conjunction with farm uses.
“Fence” means an accessory structure, including landscape planting, wood, vinyl, masonry, or any other material, designed and intended to serve as a barrier or as a means of enclosing a yard or other area, or other structure, or to serve as a boundary feature separating two or more properties.
“Festoon light” means a group of two or more incandescent light bulbs hung or strung overhead, not on a building or structure, that is exposed to persons on a public right-of-way, or that are not shaded or hooded to prevent the direct rays of the light from being visible from the property line.
“Final plat” means the diagrams, drawings, and other writing containing all the descriptions, locations, dedications, provisions and information concerning a land division.
“Fire apparatus lane” or “fire lane” means a road or other way developed to allow the passage of fire apparatus. A fire lane is not necessarily intended for vehicular traffic other than fire apparatus.
“Flag” means a piece of cloth or other flexible material attached to a staff, cord, bracket, or structure.
“Flag lot” means a lot with two distinct parts:
• The flag, which is the only building site; and is located behind another lot; and
• The pole, which connects the flag to the street; provides the only street frontage for the lot; and at any point is less than the minimum lot width for the zone. See “Lot.”
Flood Hazard Area. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Floor Area. See Development-Related Definitions for examples and excluded areas.
“Foot-candle” means a unit of illumination (light standards), equal to one lumen per square foot, or the amount of light from a source of one candela directly thrown on a square foot of surface at a distance of one foot.
Foundation Plane. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Frontage” means the dimension of a property line abutting a public or private street.
“Frontage street or road” means a minor street that parallels an arterial street or highway in order to provide access to abutting properties and minimize direct access onto the arterial or highway.
“Functional classification” means the classification given to streets by the road authority (e.g., local, collector or arterial). See Transportation-Related Definitions and SDC 3.4.100 for street standards.
“Future division plan” or “future development plan” means a document that shows lot, tract and right-of-way boundaries for all potential future phases of a land division. The plan is not binding on the city or the applicant. The purpose of the plan is to document that the design of the first phase of the plan does not preclude future phases from meeting city standards.
G. “G” Definitions.
“Garage” means a covered structure designed to provide shelter for vehicles, and which is accessory to a use in these structure types: houses, attached houses, duplexes, mobile homes, or houseboats. Carports are considered garages. Floor area adjacent to the space designed to provide shelter for vehicles, if not entirely separated from the garage area by floor-to-ceiling walls, is considered part of the garage. A garage may be attached to or detached from another structure.
“Gas station/fuel station” means a facility selling fuel and lubricants for street motor vehicles which does not include services such as oil changes and mechanical repairs to automobiles. See also definition of “Service station” and see Chapter 1.6 SDC for specific land use categories.
“Grade” means a reference plane representing the average finished grade elevation. This elevation is to be measured on the fire lane side of the building along a point six feet from the building or along the property line, whichever is closer to the building.
Grading. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Ground cover” means living or processed plant material (e.g., mulch, bark chips) that is used to cover bare ground. See Chapter 3.2 SDC, Landscaping, Street Trees, Fences and Walls.
Group Living Structure. See Residential Structure Types.
H. “H” Definitions.
“Half-story” means a story under a gable, gambrel, or hip roof, the wall plates of which on at least two opposite exterior walls are not more than two feet above the floor of such story.
“Hardscape” means nonvegetative landscape materials or installations, including pathways, decorative pavers, benches, drinking fountains, arbors, pergolas, playgrounds, plazas, and similar amenities.
“Hazardous substances” means any substance, material, or waste listed in this definition:
• Nuclear or radioactive materials or waste;
• Chemicals subject to reporting under Title III of the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act (SARA) of 1986, published July 1987, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; and
• Hazardous Materials Table in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Title 49, Part 172.101.
Historic Landmark-Related Definitions.
• “Alteration” means an addition, removal, or reconfiguration which significantly changes the character of an historic resource, including new construction in historic districts. Does not include normal maintenance and repair.
• “Contributing historic resource” means a resource that retains its architectural integrity and is within the period of significance as defined in that resource’s National Historic Register nomination application.
• “Demolition” means the razing, destruction, or dismantling of a resource to the degree that its historic character is substantially obliterated.
• “Designated landmark” means a property officially recognized by the city of Silverton, Marion County, as important in its history.
• “Designated landmark register” means the list of, and record of information about, properties officially recognized by the city of Silverton, Marion County, as important in its history.
• “Historic significance” means an individual building, structure, site, tree, landscape, or other object that has been determined to have importance because of its past relationship to any of the following:
- The importance of its designer, previous owners, or builder in local, state or national history;
- The quality of its architecture or landscaping;
- The fact that it is one of a few remaining examples of a building type that is of significance in local, state, or national history;
- Association with a significant cultural or ethnic group or the role that it has played in shaping local, state or national history.
• “Historic integrity” means the quality or wholeness of historic location, design, setting, materials, workmanship, feeling, and/or association of a resource, as opposed to its physical condition.
• “Historic resource” means a building, structure, object, site, or district which meets the significance and integrity criteria for designation as a landmark. Resource types are further described as:
- “Building” means a construction made for purposes of shelter or habitation, e.g., house, barn, store, theater, train station, garage, school, etc.
- “Structure” means a construction made for functions other than shelter or habitation, e.g., bridge, windmill, dam, highway, boat, kiln, etc.
- “Object” means a construction which is primarily artistic or commemorative in nature and not normally moveable or part of a building or structure, e.g., statue, fountain, milepost, monument, sign, etc.
- “Site” means the location of a significant event, use, or occupation which may include associated standing, ruined, or underground features, e.g., battlefield, shipwreck, campsite, cemetery, natural feature, garden, food gathering area, etc.
- “District” means a geographically defined area possessing a significant concentration of buildings, structures, objects, and/or sites which are unified historically by plan or physical development, e.g., downtown, residential neighborhood, military reservation, ranch complex, etc.
• “Historic resource of statewide significance” means buildings, structures, objects, sites, and districts which are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
• “Inventory of Historic Resources” means the record of information about resources potentially significant in the history of the city of Silverton, Marion County.
• “Noncontributing resource” means new construction or construction that has occurred in a period outside that identified as the significant period in the resource’s National Historic Register Nomination or a resource that has lost its architectural integrity through modification.
• “Relocation” means the removal of a resource from its historic context and placement in a different location.
“Home occupation” and “home occupation site” mean a business activity that is carried out on the same site as a dwelling unit, and which is accessory to the household living use on the site, subject to the provisions of Chapter 2.2 SDC, Residential (R) Districts.
“Hotel/motel” means a building or portion thereof designed and used for occupancy of transient individuals lodged with or without meals. (See ORS 446.310.)
House. See “Dwelling unit” under Residential Structure Types.
“Household” means one or more persons related by blood, marriage, civil union, legal adoption or guardianship, plus not more than five additional persons, who live together in one dwelling unit; or one or more handicapped persons as defined in the Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988, plus not more than five additional persons, who live together in one dwelling unit.
“Human-scale design/development” means site and building design elements that are dimensionally related to pedestrians, such as: small building spaces with individual entrances (e.g., as is typical of downtowns and main street developments); larger buildings that have articulation and detailing to break up large masses; narrower streets with tree canopies; smaller parking areas or parking areas broken up into small components with landscaping; and pedestrian amenities, such as sidewalks, plazas, outdoor seating, lighting, weather protection (e.g., awnings or canopies), and similar features. These features are all generally smaller in scale than those that are primarily intended to accommodate automobile traffic. (See also “Pedestrian-oriented development” under Development-Related Definitions.)
I. “I” Definitions.
Impervious Surface. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Incidental and subordinate to” means secondary to, and less apparent than, the primary use or other portion of the development.
“Infill” means the development of vacant, bypassed, or underdeveloped lands located in an area that is mainly developed.
J. “J” Definitions.
“Junk yard” means: (1) any property or establishment on which one or more persons are engaged in breaking up, dismantling, sorting, storing, distributing, buying, or selling scrap or waste materials; (2) any establishment or place of business on which two or more inoperable motor vehicles or an equivalent volume of waste or refuse are maintained, stored, bought, or sold. Includes wrecking yards, automobile graveyards, garbage dumps, and scrap metal processing facilities.
K. “K” Definitions.
“Kennel” means any location where five or more dogs or cats aged six months or older are boarded or bred. The sale of these animals may be a part of the kennel use. Establishments where animals are offered for sale as the primary use, such as pet stores, are not classified as kennels.
L. “L” Definitions.
“Land division” means the process of dividing land to create parcels or lots. See Chapter 4.3 SDC.
“Landing (stairs)” means a level part of a staircase, usually at the end of a flight of stairs.
Landmark, Historic. Historic landmark designations may include buildings, sites, trees; a portion of a building or site; statues, signs, or other objects or spaces that the city or the keeper of the National Register of Historic Places has designated or listed for their special historic, cultural, archaeological, or architectural merit. See Chapter 3.5 SDC and Historic Resource-Related Definitions for examples and related definitions.
“Landscaping” means any combination of living plants such as trees, shrubs, plants, vegetative ground cover or turf grasses, and may include structural features such as walkways, fences, benches, plazas, works of art, reflective pools, fountains or the like. Also includes irrigation systems, mulches, topsoil, and re-vegetation or the preservation, protection and replacement of trees.
“Land use” means the activity or activities that occur on a piece of land. Activities may be individually identified as primary or accessory uses. See also Chapter 1.6 SDC, Use Categories.
“Land use approval” means a land use decision for approval or approval with conditions. It includes any time limits or other restrictions that may apply to the land use decision.
Land Use District. As used in this code, a “land use district” is the same as a zoning district.
“Land use review” means an application for land use approval under Chapter 4.2 SDC, or the review of such application.
“Lane, mid-block” is similar to an alley. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Legislative. A legislative action or decision is the making of law, as opposed to the application of existing law to a particular use (e.g., adoption of, or amendment to, a comprehensive plan or development regulation). See also SDC 4.1.500, Type IV procedure.
“Livestock” means animals customarily kept on farms and includes, but is not limited to, all breeds and sizes of fowl, poultry, ostrich, emus, cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, horses, donkeys, mules, llamas, alpacas, and similar animals. See “Agriculture.”
“Living area” means the habitable floor area of a residential structure conforming to applicable building codes; typically does not include garage area, and attic and basement areas with substandard ceiling height or substandard egress.
“Loading area” means the area for the maneuvering and standing of vehicles engaged in delivering and loading goods, freight, or other articles. See also Chapter 3.3 SDC, Parking and Loading.
“Local improvement district (LID)” means a small public district formed for the purpose of carrying out local improvements (paving of streets, construction of storm sewers, development of a park, etc.). Property owners within the LID are assessed for the cost of the improvements in accordance with ORS 223.387 through 223.485.
“Longest street-facing wall” means the longest wall that faces a street. If two or more street-facing walls are of equal length, then the applicant chooses which is to be the longest street-facing wall for purposes of applying regulations of the development code. See also “Facade” and SDC 2.3.150, Commercial districts – Building orientation and commercial block layout.
“Lot” means a legally defined piece of land other than a tract that is the result of a subdivision. The following definitions for “lot” apply to the state definition of both lot (result of subdividing), and parcel (result of partitioning). See also “Ownership” and “Site.”
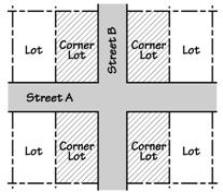
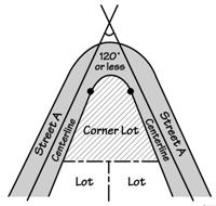
• “Corner lot” means a lot that has frontage on more than one intersecting street. A street that curves with angles that are 120 degrees or less, measured from the center line of the street, is considered two intersecting streets for the purpose of evaluating whether a lot is a corner lot. See Figures.
• “Flag lot” means a lot with two distinct parts (See Figure):
- The flag, which is the only building site; and is located behind another lot; and
- The pole, which connects the flag to the street; provides the only street frontage for the lot; and at any point is less than the minimum lot width for the zone.
• “Interior lot” means a lot that abuts other lots on two or more sides.
• “Through lot” means a lot that has frontage on two parallel or approximately parallel streets.
• “Lot lines” or “property lines” means the property lines along the edge of a lot or site.
• “Front lot line” means a lot line, or segment of a lot line, that abuts a street. On a corner lot, the front lot line is the shortest of the lot lines that abut a street. If two or more street lot lines are of equal length, then the applicant or property owner can choose which lot line is to be the front lot line. However, a through lot has two front lot lines regardless of whether the street lot lines are of equal or unequal length. See Figures.
• “Rear lot line” means a lot line that is opposite a front lot line. A triangular lot has two side lot lines but no rear lot line. For other irregularly shaped lots, the rear lot line is the longest lot line that is most nearly opposite the front lot line. See Figures.
• “Side lot line” means a lot line that connects front and rear lot lines. On a corner lot, the longer lot line that abuts a street is a side lot line. See Figures.
• “Side street lot line” means a lot line that is both a side lot line and a street lot line. See Figures.
• “Street lot line” means a lot line, or segment of a lot line, that abuts a street. “Street lot line” does not include lot lines that abut an alley. On a corner lot, there are two (or more) street lot lines. “Street lot line” can include front lot lines and side lot lines. See Figures.
See lot types and lot line graphics on the following pages.
Corner Lots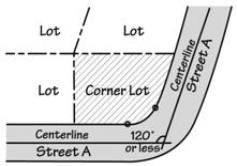
Flag Lot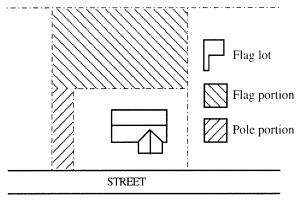
Front and Side Lot Lines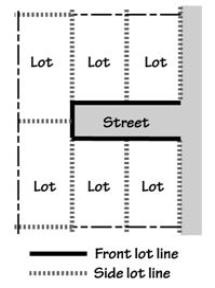
Street Lot Lines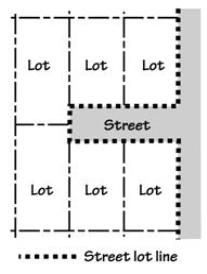
Lot Lines on Irregular Lots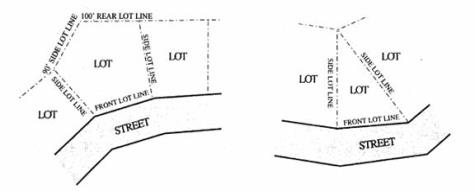
“Lot of record” means a plot of land:
• That was not created through an approved subdivision or partition;
• That was created and recorded before October 6, 2008; and
• For which the deed, or other instrument dividing the land, is recorded with the appropriate county recorder.
See Chapter 5.3 SDC, Lots of Record.
Lot, Double-Frontage. See “Lot” and “Through lot.”
“Lot area” means the total surface area (measured horizontally) within the boundary lines of a lot.
“Lot coverage” means the total area of a lot covered by the foundation plane, as allowed by the applicable land use district development standards. Does not include overhangs, eaves, projecting (e.g., cantilevered) decks, and similar projections beyond the foundation plane.
Lot Line Adjustment. See “Property line adjustment.”
M. “M” Definitions.
“Main/primary building entrance” means the entrance to a building that most pedestrians are expected to use. Generally, each building has one main entrance. Main entrances are the widest entrance of those provided for use by pedestrians. In multitenant buildings, main entrances open directly into the building’s lobby or principal interior ground level circulation space. When a multitenant building does not have a lobby or common interior circulation space, each tenant’s outside entrance is a main entrance. In single-tenant buildings, main entrances open directly into lobby, reception, or sales areas.
“Major partition” means a partition which includes the creation of a road or street and which does not result in the creation of more than two or three lots within a calendar year. See also “Partition” and “Subdivision.”
“Major remodeling” means projects where the floor area is being increased by 50 percent or more, or where the cost of the remodeling is greater than the assessed value of the existing improvements on the site. “Assessed value” is the value shown on the applicable county assessment and taxation records for the current year.
“Maneuvering area/aisle” means the driving area in a parking lot where motor vehicles are able to turn around and access parking or loading spaces.
Manufactured Dwelling. See Residential Structure Types.
Manufactured Home. See Residential Structure Types.
“Manufactured home/dwelling park” means any place where four or more manufactured dwellings are located within 500 feet of one another on a lot, tract or parcel of land under the same ownership, the primary purpose of which is to rent or lease space or keep space for rent or lease to any person for a charge or fee paid or to be paid for the rental or lease or use of facilities or to offer space free in connection with securing the trade or patronage of such person. “Manufactured dwelling park” does not include a lot or lots located within an approved subdivision being rented or leased for occupancy by no more than one manufactured dwelling per lot. See also ORS Chapter 446.
“Marijuana processor” means a facility licensed by the Oregon Liquor Control Commission or registered by the Oregon Health Authority to process, compound or convert marijuana into cannabinoid products, cannabinoid concentrates or cannabinoid extract. Marijuana processing is a manufacturing and production use.
“Marijuana producer” means a facility that is licensed by the Oregon Liquor Control Commission or the Oregon Health Authority to manufacture, plant, cultivate, grow or harvest marijuana. Marijuana production is an agricultural use.
“Marijuana retailer” means a facility licensed by the Oregon Liquor Control Commission who sells marijuana to a consumer. Marijuana retailers are a retail sales and services use.
“Marijuana wholesaler” means a facility licensed by the Oregon Liquor Control Commission who purchases marijuana items in this state for resale to a person other than a consumer. Marijuana wholesalers are a retail sales and services use.
“Master road plan” means the plan(s) adopted by the council of the city according to the procedures provided for this title.
“Medical marijuana dispensary” means a facility registered with the Oregon Health Authority or for which an application has been submitted to the OHA that transfers usable marijuana, immature marijuana plants, seeds, and cannabinoid products, concentrates and extracts to registrants and primary caregivers. Dispensaries also receive transfers of cannabinoid products, concentrates and extracts from marijuana processing sites. Dispensaries receive transfers of usable marijuana, immature marijuana plants and seeds from registrants and primary caregivers. Medical marijuana dispensaries are a retail sales and services use.
“Medical marijuana grow site” means a specific location registered by the OHA used by a medical marijuana grower to manufacture, plant, cultivate, grow, or harvest marijuana or dry marijuana leaves or flowers for medical use by a specific patient.
“Ministerial” means a routine administrative action or decision that involves little or no discretion. The issuance of a building permit is generally such an action. See SDC 4.1.200, Type I procedure (ministerial).
“Mitigation” means to avoid, rectify, repair, or compensate for negative impacts that result from other actions (e.g., improvements to a street may be required to mitigate for transportation impacts resulting from development).
“Mixed-use” means the combination on a site of residential uses with commercial (e.g., office, retail, or services), civic, or industrial uses.
Mobile Home. See Residential Structure Types.
“Mobile home park” means two or more mobile homes that are located on a single site for 30 days or more and intended for residential use. “Mobile home park” does not include sites where unoccupied mobile homes are offered for sale or lease. See also “Recreational vehicle park.”
“Mobile home space” means the area occupied by a mobile home and its accessory uses and structures in a mobile home park.
Motor Home. See “Recreational vehicle” under Vehicle Types.
Motor Vehicle. See Vehicle Types.
Multidwelling Development. See Residential Structure Types.
Multidwelling Structure. See Residential Structure Types.
“Multi-use pathway” means a transportation facility serving pedestrians, bicycles and, where allowed, equestrian usage.
N. “N” Definitions.
“Natural hazard” means natural areas that can cause dangerous or difficult development situations. For example, natural hazard areas include steep slopes, unstable soils, and areas prone to landslides, floodways and floodplains.
Natural Resource Areas/Natural Resources. See “Sensitive lands” under Environment-Related Definitions.
“Neighborhood” means a residential area usually having distinguishing character or geography.
“Nonconforming development” means an element of a development, such as a setback, height, or parking area, that was created in conformance with development regulations but which subsequently, due to a change in the zone or zoning regulations, is no longer in conformance with the current applicable development standards. “Nonconforming development” includes development that is over a maximum allowed amount of floor area, as long as the development does not include an amount of floor area that is specifically prohibited by the current development standards. See Chapter 5.2 SDC.
“Nonconforming residential density” means a residential use that is an allowed use in the zone and that was constructed at a lawful density, but which subsequently, due to a change in the zone or zoning regulations, now has greater density than is allowed in the zone. See Chapter 5.2 SDC.
“Nonconforming situation” means a nonconforming residential density, nonconforming development, or nonconforming use. A situation may be nonconforming in more than one aspect. For example, a site may contain a nonconforming use and also have some nonconforming development. See also “Nonconforming development,” “Nonconforming residential density,” and “Nonconforming use.” See Chapter 5.2 SDC.
“Nonconforming use” means a use that was allowed by right when established or a use that obtained a required land use approval when established, but that subsequently, due to a change in the zone or zoning regulations, the use or the amount of floor area of the use is now prohibited in the zone. See Chapter 5.2 SDC.
“Nonnative invasive plants” means plants listed under current Oregon State University Extension Service Bulletins as nonnative, invasive plants in Oregon.
O. “O” Definitions.
“Off-street parking” means all off-street areas designed, used, required or intended to be used for the parking of motor vehicles. See Chapter 3.3 SDC for parking standards.
“On-street parking” means parking in the street right-of-way, typically in parking lanes or bays. Parking may be “parallel” or “angled” in relation to the edge of the right-of-way or curb. See Chapter 3.3 SDC for parking standards.
“Open space (public/private/dedicated in common)” means land that has been dedicated in common to the ownership within a development or to the public, or privately held, specifically for the purpose of providing places for recreation, conservation or other open space uses. Includes parks and mini-parks and incorporates the classifications found in the city of Silverton parks and recreation master plan.
“Orientation” means to cause to face toward a particular point of reference (e.g., “a building oriented to the street”). See also “Pedestrian-oriented development” under Development-Related Definitions.
“Outdoor commercial use” means a use supporting a commercial activity that provides goods or services, either wholesale or retail, where the amount of site area used for outdoor storage of materials or display of merchandise exceeds the total floor area of all buildings on the site. Examples of outdoor commercial uses include automobile sales or services, nurseries, lumber yards and equipment rental businesses.
“Outlying commercial pad” means a small, free-standing commercial use (e.g., bank, restaurant, gas station, car wash, etc.) adjacent to larger commercial use(s), either on the same parcel or on a separate parcel, and typically oriented and designed to take advantage of internal driveways and surface parking that the uses share; may include a drive-up/drive-through facility.
Overlay Zone/District. Overlay zones impose and/or relax requirements of an underlying land use district, or base zone, where characteristics of the land or neighborhood, or the types of development planned for an area, require special regulations. See Chapters 2.5, 2.6, 2.7 and 2.8 SDC.
“Owner” means the owner of the title to real property or the contract purchaser of real property of record, as shown on the latest assessment records in the office of the county assessor. “Owner” also includes a deed holder or contract purchaser whose name does not appear in the latest assessment records, but who presents to the city a copy of a deed or contract of sale showing date, book, and page of recording.
“Ownership” means one or more contiguous lots that are owned by the same person, partnership, association, or corporation. “Ownership” also includes lots that are in common ownership but are separated by a right-of-way. See also “Lot” and “Site.”
P. “P” Definitions.
“Parcel” means a legally defined area of land created through a partition.
“Parking” means areas designed and developed in accordance with Chapter 3.3 SDC for automobile or bicycle parking, as applicable.
“Parking area” means all the area devoted to the standing, maneuvering, and circulation of motor vehicles. Parking areas do not include driveways or areas devoted exclusively to nonpassenger loading.
“Parking bay” means a parking area with a concrete curb forming one side of the parking stall(s). Bays are typically adjacent and accessible to a sidewalk or walkway within a development.
“Parking lot perimeter” means the boundary of a parking lot area that usually contains a landscaped buffer area.
“Parking space” means a space designed to provide standing area for a motor vehicle. See Chapter 3.3 SDC for parking space standards.
Parking versus storage. “Parking” is to leave a motor vehicle for a temporary time, no longer than 72 hours. “Storage” is to place or leave in a location for maintenance, repair, sale, rental, or future use more than 72 hours in the future. See also “Exterior display.”
“Partition” means to divide an area or tract of land into two or three parcels within a calendar year when such area or tract of land exists as a unit or contiguous units of land under single ownership at the beginning of such year. (See ORS 92.010(8))
Pathway. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Pedestrian Amenity(ies). See Development-Related Definitions for examples and related definitions.
“Planning office” means the Silverton City Hall, Silverton, Oregon.
“Planter strip” means a landscaped area for city-approved street trees and other plantings within the public right-of-way, usually a continuous planter area between the street and a sidewalk. See also “Tree well.” Refer to the city of Silverton list of recommended trees.
“Plat” means diagrams, drawings and other writing containing all the descriptions, locations, dedications, provisions, and information concerning a land division. This term includes the state law definitions of “partition plat” and “subdivision plat.” See also Chapter 4.3 SDC, Land Divisions and Property Line Adjustments.
“Plaza” means an area generally open to the public on a controlled basis and used for passive recreational activities and relaxation. Plazas are paved areas typically provided with amenities, such as seating, drinking and ornamental fountains, art, trees, and landscaping for use by pedestrians. See also “Pedestrian amenities” under Development-Related Definitions.
“Practicable” means capable of being done after taking into consideration cost, existing technology, and logistics in light of overall project purposes.
“Primary structure” means a structure or combination of structures of chief importance or function on a site. In general, the primary use of the site is carried out in a primary structure. The difference between a primary and accessory structure is determined by comparing the size, placement, similarity of design, use of common building materials, and the orientation of the structures on a site.
“Primary use” means an activity or combination of activities of chief importance on the site; one of the main purposes for which the land or structures are intended, designed, or ordinarily used. A site may have more than one primary use.
“Project” means an existing or proposed use or development.
“Project, major” means a project that requires design review (Chapter 4.2), subdivision or partition review (Chapter 4.3), conditional use review (Chapter 4.4), or planned development review (Chapter 4.5).
“Project, minor” means a project that requires land use review but does not require design review (Chapter 4.2), subdivision or partition review (Chapter 4.3), conditional use review (Chapter 4.4), or planned development review (Chapter 4.5).
“Property line adjustment” means the relocation of a single common property line between two abutting properties, in conformance with ORS 92.010(11). See Figure.
Property Line Adjustment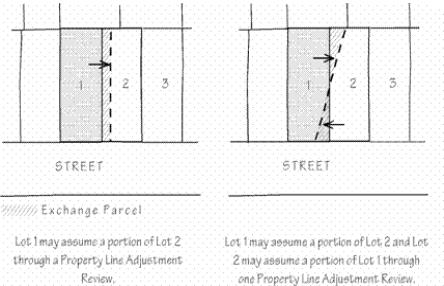
Property Line, Front, Rear, Interior Side, Street Side. See “Lot lines” under “Lot.”
“Public access easement” means an easement recorded for the purpose of providing vehicle, bicycle, and/or pedestrian access from a public street to a parcel across intervening property under separate ownership from the parcel being provided access. See also Transportation-Related Definitions.
“Public safety facility” means a facility necessary to respond to an immediate hazard to the public health and safety, and that is owned, leased, or operated by the city of Silverton. Public safety facilities include fire and police stations, flood control facilities, water towers and pump stations needed for emergency service, and emergency communication broadcast facilities.
“Public improvements” means development of public infrastructure, as required by the city, county, special district, or road authority, as applicable. See Chapter 3.4 SDC.
“Public right-of-way” means land dedication or easement conveyance to the city or other public entity for public use; typically for streets, utilities, parkland and/or similar facilities. Permanent structures, objects and buildings are not allowed to project over or encroach into public rights-of-way, except as allowed by the city for landscaping and trees.
Q. “Q” Definitions.
“Quasi-judicial” means an action or decision that requires substantial discretion or judgment in applying the standards or criteria of this code to the facts of a development proposal, and usually involves a public hearing. See SDC 4.1.400, Type III procedure.
R. “R” Definitions.
“Recreation camp” means: (1) An area devoted to facilities and equipment for recreation purposes, including swimming pools, tennis courts, playgrounds, and similar uses, either open to the public upon payment of a fee, or limited to private membership; (2) an area designated by the landowner for picnicking or overnight camping and offered to the general public, with or without a fee or charge. (See ORS Chapter 446.)
Recreational Vehicle. See Vehicle Types.
“Recreational vehicle park” means a commercial use providing space and facilities for motor homes or other recreational vehicles for recreational use or transient lodging. There is no minimum required stay in a recreational vehicle park. Uses where unoccupied recreational vehicles are offered for sale or lease, or are stored, are not included as recreational vehicle parks. See also “Mobile home park.”
“Residence” means the same as “Dwelling unit.” See under Residential Structure Types.
Residential Structure Types.
• “Accessory dwelling unit” means a second dwelling unit created on a lot with a single-family house, attached house, or manufactured home outside of a manufactured home/dwelling park. The second unit is created auxiliary to, and is always smaller than, the single-family house, attached house, or manufactured home.
• “Attached duplex” means a duplex located on its own lot that shares one or more common or abutting walls with one other duplex (for a total of four dwelling units). The common or abutting wall must be shared for at least 50 percent of the length of the side of the dwelling.
• “Attached house (townhome or rowhouse)” means a dwelling unit located on its own lot that shares one or more common or abutting walls with one or more dwelling units. The common or abutting wall must be shared for at least 50 percent of the length of the side of the dwelling. An attached house does not share common floor/ceilings with other dwelling units. An attached house is also called a rowhouse or a common-wall house.
• “Condominium” means a building or group of buildings in which dwelling units, offices, or floor area are owned individually, and the structure, common area, and facilities are owned by all the owners on a proportional, undivided basis.
• “Cottage” means a small house, generally containing not more than 1,200 square feet of floor area.
• “Cottage cluster” means a group of two or more cottages on one lot.
• “Duplex” means two primary dwelling units on a lot in any attached or detached configuration. This definition does not include a single-family house, attached house or manufactured home developed with an accessory dwelling unit.
• “Dwelling unit” means a building, or a portion of a building, that has independent living facilities including provisions for sleeping, cooking, and sanitation, and that is designed for residential occupancy by a group of people. Buildings with more than one set of cooking facilities are considered to contain multiple dwelling units or accessory dwelling units, unless the additional cooking facilities are clearly accessory to the primary use, such as an outdoor grill.
• “Group living structure” means a structure that contains sleeping areas and at least one set of cooking and sanitary facilities that is used as a residence for group living uses:
- “Residential facility/group care facility” means a residence for six to 15 physically, mentally or socially dependent/disabled persons, and for staff persons. The facility may provide residential care alone, or in conjunction with training or treatment. This definition includes the state definition of “residential facility” but also includes, but is not limited to, nursing homes, convalescent homes, retirement homes, assisted care facilities, etc.
- “Residential home/group care home” means a residence for five or fewer physically, mentally or socially dependent/disabled persons, and for staff persons. The residence may provide residential care alone, or in conjunction with training or treatment. This definition includes the state definition of “residential home.”
- “Residential institution/group care institution” means a residence for more than 15 physically, mentally or socially dependent/disabled persons, and for staff persons. The facility may provide residential care alone, or in conjunction with training or treatment. This definition includes the state definition of “residential facility” but also includes, but is not limited to, nursing homes, convalescent homes, retirement homes, assisted care facilities, etc.
• “Manufactured dwelling” means a residential trailer, mobile home or manufactured home. “Manufactured dwelling” does not include any building or structure constructed to conform to the State of Oregon Structural Specialty Code, the Low-Rise Residential Dwelling Code or the Small Home Specialty Code.
- “Manufactured home” means a structure constructed for movement on the public highways that has sleeping, cooking and plumbing facilities, that is intended for human occupancy, that is being used for residential purposes and that was constructed in accordance with federal manufactured housing construction and safety standards and regulations in effect at the time of construction, that was constructed after June 15, 1976.
- “Mobile home” means a structure constructed for movement on the public highways that has sleeping, cooking and plumbing facilities, that is intended for human occupancy, that is being used for residential purposes and that was constructed between January 1, 1962, and June 15, 1976, and met the construction requirements of Oregon mobile home law in effect at the time of construction.
- “Residential trailer” means a structure constructed for movement on the public highways that has sleeping, cooking and plumbing facilities, that is intended for human occupancy, that is being used for residential purposes and that was constructed before January 1, 1962.
• “Multidwelling development” means a grouping of individual structures where each structure contains one or more dwelling units and that includes three or more total dwelling units. The land underneath the structures is not divided into separate lots. A multidwelling development project may include an existing single-dwelling detached building with one or more new detached structures located to the rear or the side of the existing house. It might also include a duplex in front with either one or more single-dwelling houses behind or one or more duplex units or multidwelling structures behind. There is no requirement for the structures on the sites to be attached.
• “Multidwelling structure” means a structure that contains three or more dwelling units that share common walls or floor/ceilings with one or more units. The land underneath the structure is not divided into separate lots. “Multidwelling structure” includes structures commonly called garden apartments, apartments, and condominiums.
• “Senior housing” means housing designated and/or managed for persons over a specified age. Specific age restrictions vary.
• “Single-family house/dwelling” means a detached dwelling unit located on its own lot.
• “Single-room-occupancy housing (SRO)” means a structure that provides living units that have separate sleeping areas and some combination of shared bath or toilet facilities. The structure may or may not have separate or shared cooking facilities for the residents. SRO includes structures commonly called residential hotels and rooming houses.
• “Zero-lot-line house” means a single-family detached dwelling with one “zero” side yard setback.
“Review body” means the person or group who is assigned to make decisions on land use reviews, whether initially or on appeal. “Review body” includes the community development director, the planning commission, and the city council.
Right-of-Way. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Riparian Areas. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Roadway; Road Authority. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Rooftop Structures. Include towers, spires, steeples and other structures when built according to Section 1509 of the International Building Code. (May extend 20 feet past the roof height limit of this code when approved through a conditional use, and subject to fire department approval.)
Rowhouse (Rowhome). See Residential Structure Types.
S. “S” Definitions.
Senior Housing. See Residential Structure Types.
Sensitive Lands. See Environment-Related Definitions.
“Service station” means a gas station that also offers services such as oil changes and mechanical repairs to automobiles.
“Setback” or “setback yard” means the minimum distance required between a specified object, such as a building, and another point, measured from lot lines to a specified object. Typically, a setback refers to the minimum distance (yard dimension) from a building to a specified property line.
Shared Driveway. See Development-Related Definitions.
Shared Parking. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Shipping container or converted vehicle” means a shipping container, bus, rail car, or other vehicle originally intended for storage or moving of people or goods that has been converted for residential use.
Shopping Street. See Development-Related Definitions.
Shoreline. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Sign. Signs are regulated under Chapter 15.16 SMC.
“Significant trees” and “significant vegetation” mean any tree, shrub, or combination thereof, meeting the threshold standards in SDC 3.2.200, and those that are located within a sensitive land area as identified by the comprehensive plan or any refinement of the comprehensive plan, or as inventoried through the development review process. See also Environment-Related Definitions in this chapter and SDC 3.2.200, Landscape conservation.
Single-Room-Occupancy Housing (SRO). See Residential Structure Types.
Site. For land divisions, property line adjustments, and lot consolidations, the site is the lot, lot of record, parcel, or tract proposed to be divided or reconfigured. For all other purposes, the site is an ownership, except as follows:
• If a proposed development includes multiple ownerships, then the site is the combined area of all the ownerships.
• If a proposed development includes only a portion of an ownership, and the balance of the ownership is vacant, then the applicant may choose to define the site as the portion of the ownership that is proposed for development.
• If a proposed development includes only a portion of an ownership, and there is other development on the ownership, then the applicant may choose to define the site as the portion of the ownership that is currently developed plus the portion proposed for development.
“Site frontage” means the part of a site that abuts a street. See also “Block frontage.”
“Specific area plan” means an adopted plan for a subarea of the city and/or urban growth area providing a framework and standards for future land uses, densities, blocks, typical lot patterns, public improvements and streets, and site design; may also include architectural design guidelines or standards.
Standards and Criteria. Both are code requirements for how to develop uses and structures on land. A “standard” is a quantitative requirement, or a qualitative requirement that is used in interpreting a subjective criterion. (Example criterion: All developments subject to design review shall comply with the Article 3 parking standards. Standard: Medical and dental office uses must provide one vehicle parking space for each x square feet of gross floor area.)
“Steep slopes” means slopes exceeding 12 percent or as regulated by hillside development regulations.
Step-Down. See Building Height in Development-Related Definitions.
Storefront Character. See Development-Related Definitions.
Stormwater Facility. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Stormwater management system” means a stormwater facility (e.g., conveyance, detention/retention, treatment system or outfall).
“Story” means a portion of a building between any floor and the next floor or ceiling above. If the floor level directly above a basement or unused under-floor space is more than six feet above grade for more than 50 percent of the total perimeter or is more than 10 feet above grade at any point, such basement or unused under-floor space shall be considered as a story.
Stream. See Environment-Related Definitions.
Street. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Street Connectivity. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Street-Facing Facade/Wall. See Development-Related Definitions.
Street Furniture/Furnishings. See Development-Related Definitions.
Structure. See Development-Related Definitions.
“Subdivision” means to divide land into four or more lots within a single calendar year. See also Chapter 4.3, Land Divisions and Property Line Adjustments, and ORS 92.010(13).
“Surface water management” means storm drainage and/or storm drainage facilities that are functioning in accordance with the city of Silverton storm drainage master plan.
Swale. See Development-Related Definitions.
T. “T” Definitions.
“Tangent” means meeting a curve or surface in a single point.
“Terrace” means a porch or promenade supported by columns, or a flat roof or other platform on a building.
Through Lot. See “Lot.”
Through Street. See Transportation-Related Definitions.
Top of Bank. See Environment-Related Definitions.
“Topographical constraint” means where existing slopes, landforms (e.g., streams, canals, rock outcropping, etc.) or manmade features (e.g., embankment or berm) make conformance with a code standard impracticable.
Townhome. See Residential Structure Types.
“Tract” means a piece of land within a platted subdivision reserved for open space, utility corridor, recreation facilities, sensitive lands, or other purpose; may be dedicated to a homeowners’ association or other entity for maintenance.
Transitional Shelter Communities. Per ORS 446.265. Accommodations that may consist of separate facilities, in the form of sleeping pods or other approved structures, for use as living units by one or more individuals or by families. The person establishing the accommodations shall provide access to water and toilet through separate or shared facilities, and may provide access to shower, laundry, cooking, telephone or other services either through separate or shared facilities. The accommodations shall provide parking facilities and walkways. Transitional housing accommodations shall be limited to persons who lack permanent shelter and cannot be placed in other low income housing.
Transportation-Related Definitions.
• “Access” means a way or means of approach to provide pedestrian, bicycle, and/or motor vehicular entrances or exits to a property.
• “Access easement” means an easement recorded for the purpose of providing vehicle, bicycle, and/or pedestrian access from a public street to a parcel across intervening property under separate ownership from the parcel being provided access. “Cross access” is a service drive providing vehicular access between two or more separate sites, so that the driver need not enter the public street system between sites.
• “Access management” means the systematic control of the location, spacing, design, and operation of driveways, median openings, interchanges, and street connections to a roadway to minimize conflicts between turning and through vehicles, bicyclists and pedestrians. The purpose of access management is to provide vehicular access to land development in a manner that preserves the safety and efficiency of the transportation system. Public facility measures to support access management include roadway design applications, such as median treatments and auxiliary lanes, and the appropriate spacing of traffic signals. Measures that may be included as conditions of approval for development decisions include but are not limited to (1) standards such as minimum spacing of driveways and on-site vehicle storage requirements, (2) mitigations related to site conditions such as right-in-right-out-only approaches, medians, dedicated turn lanes, and shared access approaches, and (3) provision for future opportunities for mitigation by land dedication or easement.
• “Access spacing” or “intersection spacing” means the minimum required distance from an intersection of a public or private street to the nearest driveway or other access connection, measured from the closest edge of the pavement of the intersecting street to the closest edge of the pavement of the connection along the traveled way.
• “Access way” means a walkway or multi-use pathway providing a through connection for pedestrians between two streets, between two lots, or between a development and adjoining public right-of-way. It may be an access way for pedestrians and bicyclists (with no vehicle access), or a walkway on public or private property (i.e., with a public access easement). See also “Walkway.”
• Accessible. Two meanings are possible depending on the specific code provision. In general, “accessible” means approachable by pedestrians, vehicles or other transportation modes, as applicable. “Accessible” may also mean approachable and usable by people with disabilities, in conformance with the federal Americans with Disabilities Act. Either or both definitions may apply in a particular situation. See “Accessible route.”
• “Accessible route” means a route that can be used by a disabled person using a wheelchair and that is also usable by people with other disabilities.
• “Alley” means a right-of-way that provides vehicle access to a lot or common parking area. Generally, alleys provide secondary vehicle access; however, where vehicle access from the street is not allowed, not possible, or not desirable the alley may provide primary vehicle access.
• “Arterial” means the highest order classification of streets; includes highways and other major streets with limited or no direct access from adjoining properties. Also includes streets designated as arterial within the city of Silverton transportation system plan.
• Bicycle Facility. There are different types of bicycle facilities. In general, a “bicycle facility” is a public or private way designed for and dedicated to bicycle use. It may consist of a road, a lane within or on the shoulder of a road, a path, a multi-use path, or other way that is specifically designated for bicycle travel or shared bicycle/pedestrian travel.
• “Boulevard” means a street with broad open space areas; typically with planted medians. See standards under SDC 3.4.100.
• “Bus stop” means a location where bus service stops to load and unload passengers. For purposes of measuring, the bus stop is the location of a sign denoting the bus stop.
• “Collector” means a type of street that serves traffic within commercial, industrial, and residential neighborhood areas, connecting local neighborhood or district streets to the arterial network and is part of the street grid system. Also includes streets designated as “collector” within the city of Silverton transportation system plan.
• “Common green” means a courtyard that provides for pedestrian and bicycle access, but not vehicle access, to abutting property, and generally provides a common area for use by residents. A common green may function as a community yard. Hard and soft landscape features may be included in a common green, such as ground cover, trees, shrubs, surfaced paths, patios, benches, or gazebos.
• “Curb cut” means a driveway opening delineated by a concrete apron along a street.
• “Dead-end street” means a street that connects to another street at only one end and does not have a city-approved turnaround on its other end. A pedestrian connection may extend from the end of a dead-end street to connect with another street of any type, or with another pedestrian connection.
• “Lane, mid-block” means a narrow, limited use roadway facility, similar to an alley in design, usually used to access a limited number of dwelling units.
• “Level of service (LOS)” means a quantitative standard for transportation facilities describing operational conditions. Level of service may be described for intersections (signalized or unsignalized) or street segments (between signalized intersections).
• “Local” means a type of street that serves traffic within a residential neighborhood, connecting residential streets as part of a grid system. Also includes streets designated as “local” within the Silverton transportation system plan.
• “Multi-use pathway” means a transportation facility serving pedestrians, bicycles and, where allowed, equestrian usage.
• “Pathway” means a walkway conforming to Chapter 3.1 SDC that is not within a street right-of-way.
• “Public access easement” means an easement granted to the public for all the purposes for which a public sidewalk may be used, including but not limited to pedestrian and bicycle travel.
• “Rail right-of-way” means a public or private right-of-way, for the purpose of allowing rail travel.
• “Right-of-way” means a public use area that allows for the passage of people or vehicles. “Right-of-way” includes passageways such as freeways, pedestrian connections, alleys, and all streets. A right-of-way may be dedicated or deeded to the public for public use and under the control of a public agency, or it may be privately owned. A right-of-way that is not dedicated or deeded to the public may be in a tract.
• “Roadway” means the portion of a right-of-way that is improved for motor vehicle travel. Roadway includes vehicle travel lanes and on-street parking areas. “Roadway” does not include area devoted to curbs, parking strips, or sidewalks.
• “Road authority” means the city (typically the public works director or his/her designee) or other agency (e.g., Oregon Department of Transportation, Marion County, a special purpose district, or other agency) with jurisdiction over a road or street.
• “Sidewalk” means a paved walkway within a public street right-of-way that is generally located adjacent to and separated from the roadway by a curb or curb and planter strip.
• “Sight distance” means the unobstructed viewing distance measured from one object or location to another object or location, usually required for the purpose of traffic safety.
• “Street” means a right-of-way that is intended for motor vehicle, pedestrian or bicycle travel or for motor vehicle, bicycle or pedestrian access to abutting property. For the purposes of this code, “street” does not include alleys, rail rights-of-way that do not also allow for motor vehicle access, or freeways and their onramps.
• “Street connectivity” is expressed as the number of street and/or access way connections within a specific geographic area. Higher levels of connectivity provide for more direct transportation routes and better dispersion of traffic, resulting in less traffic on individual streets and potentially slower speeds through neighborhoods.
• “Street stub” means a temporary street ending where the street will be extended through adjacent property in the future, as that property develops. Not a permanent street end or dead-end street.
• “Street tree” means a city-approved tree planted in a planter strip or tree well in a city right-of-way. See the city of Silverton recommended list of trees.
• “Through street” means a street that connects to other streets at both ends.
• “Transportation mode” means the method of transportation (e.g., automobile, bus, walking, bicycling, train, etc.).
• “Turnaround” means a vehicle-maneuvering area at the end of a dead-end street (e.g., hammerhead, cul-de-sac, or other configuration) that allows for vehicles to turn around. See SDC 3.4.100 for related standards.
• “Walkway” means a sidewalk or pathway, including access ways, providing a pedestrian connection that is improved to city standards, or to other roadway authority standards, as applicable. See also “Access way,” “Pathway,” and “Sidewalk.”
Travel Trailer. See Vehicle Types.
“Travel trailer/recreational vehicle park/campground” means a lot or parcel on which two or more travel trailers, recreational vehicles, motor homes, tent trailers, tent sites, campers, and/or similar vehicles or devices are permitted outright, with or without a charge or fee.
“Tree well” means a planter area cut out of a sidewalk within the street furnishing zone, planted with a street tree and including ground cover or a grate cover; typically used in commercial districts where on-street parking or pedestrian traffic makes the use of a planter strip impracticable.
U. “U” Definitions.
“Use” means the purpose for which land or a structure is designed, arranged, intended, occupied, or maintained. See also Chapter 1.6 SDC, Use Categories.
Utilities. For the purposes of this code, “utilities” are telephone, cable, natural gas, electric, and telecommunication facilities.
V. “V” Definitions.
“Vacate plat/street” means to abandon a subdivision or street right-of-way. For example, vacation of a public right-of-way that is not needed or cannot be used for a street or other public purpose. Vacation of a plat typically returns the property to the adjoining owners and restores it to an undivided condition and ownership.
“Vacation home rental” means a commercial use of a single-family or duplex dwelling unit where the unit is rented for periods of time of 28 or fewer consecutive days.
“Variance” means an administrative or quasi-judicial decision to lessen or otherwise modify the requirements of this code. See Chapter 5.1 SDC.
Vehicle Areas. See Development-Related Definitions.
Vehicle Types.
• “Motor vehicle” means vehicles that have their own motive power and that are used for the transportation of people or goods on streets. “Motor vehicle” includes motorcycles, passenger vehicles, trucks, and recreational vehicles, except all-terrain vehicles, off-road vehicles, snowmobiles, and similar vehicles are not allowed on streets.
• “Passenger vehicle” means a motor vehicle designed to carry 10 persons or less including the driver. “Passenger vehicles” are passenger cars and multipurpose passenger vehicles as defined by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration in Title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Chapter V, Section 571.3. See also “Recreational vehicle” and “Truck.”
• “Recreational vehicle” means a vehicle with or without motive power that is designed for sport or recreational use, or that is designed for human occupancy on an intermittent basis. “Recreational vehicle” is divided into two categories as follows:
- “Motor home” includes motorized vehicles designed for human occupancy on an intermittent basis. A camper is considered a motor home when it is on the back of a pick-up or truck. Motor homes are regulated as trucks unless the regulations specifically indicate otherwise. See also “Truck.”
- “Accessory recreational vehicle” includes nonmotorized vehicles designed for human occupancy on an intermittent basis such as vacation trailers and fifth-wheel trailers. A camper is considered an accessory recreational vehicle when it is standing alone. “Accessory recreational vehicle” also includes vehicles designed for off-road use, such as all-terrain vehicles, dune buggies, and recreational boats.
• “Travel trailer” means a vacation structure or self-propelled vehicle equipped with wheels for street or highway use; intended for human occupancy; equipped with plumbing, sink or toilets; used for vacation and recreational purposes; and not used as a residence. (See ORS 446.003(5), (24).)
• “Truck” means a motor vehicle that is designed primarily for the movement of property or special purpose equipment, or a motor vehicle that is designed to carry more than 10 persons. “Truck” includes vehicles commonly called trucks, pick-ups, delivery vans, buses, motor homes and other similar vehicles. See also National Highway Traffic Safety Administration in Title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Chapter V, Section 571.3.
- “Light truck” means trucks and similar vehicles with single rear axles and single rear wheels.
- “Medium truck” means trucks and similar vehicles with single rear axles and dual rear wheels. Truck tractors are in the heavy truck category.
- “Heavy truck” means trucks, including truck tractors, and similar vehicles with two or more rear axles and all truck tractors and truck trailers.
• “Truck trailer” means trucks including utility trailer(s).
• “Utility trailer” means a vehicle designed to be pulled by a motor vehicle that is used to carry property, trash, or special equipment and that is 16 feet or less in length. Boat trailers are included as utility trailers. Utility trailers that are longer than 16 feet are considered industrial vehicles and are regulated as heavy trucks.
“Vision clearance area” means those areas near intersections of roadways and motor vehicle access points where a clear field of vision is necessary for traffic safety and to maintain adequate sight distance. See standards in SDC 3.1.200.
W. “W” Definitions.
“Waste collection areas” include areas set aside or designed to be used for garbage collection and collection of materials for recycling. “Waste collection areas” include areas occupied by dumpsters and other solid waste receptacles.
“Window” means a transparent or semi-transparent (not more than 50 percent opaque) glazing on a building facade. For the purpose of this code, a window may be a display window (e.g., for merchandise, art, etc.) that is integral to a building design, but a window is not a display box mounted onto the exterior of a building.
“Wireless communication equipment” means cellular towers, antennas, monopoles, and related facilities used for radio signal transmission and receiving.
X. “X” Definitions.
Reserved.
Y. “Y” Definitions.
“Yard” means the area defined by setbacks (i.e., between the setback line and nearest property line). See “Setbacks.”
Z. “Z” Definitions.
Zero-Lot-Line House. See Residential Structure Types. (Ord. 21-04 § 1, 2021; Ord. 18-22 § 1, 2018; Ord. 16-04 § 1, 2016; Ord. 16-01 § 1, 2016; Ord. 14-01 § 1 (Exh. A), 2014; Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010; Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)


