Chapter 2.8
PUBLIC (/P) OVERLAY DISTRICT
Sections:
2.8.130 Abandoning use – Transfer of ownership.
2.8.160 Public overlay district standards.
2.8.170 Public overlay design standards.
2.8.180 Special use standards.
2.8.110 Purpose.
The public overlay district (/P) is intended to identify those properties that are in public, semi-public, or governmental ownership. These properties generally contain uses that are considered essential public services or otherwise allow uses, services or facilities that enhance the livability and quality of life for the Silverton general public. These uses, facilities or services are generally noncommercial and/or not-for-profit. The intent of the public (/P) overlay district is to recognize existing facilities, allow these sites to continue to be used to meet public needs, and when these facilities, uses, or sites are no longer needed, provide a system that allows for transfer into private ownership in accordance with established zoning. Typical types of uses that may occur within the public overlay zone are: fairground; exposition center; conference center; overnight lodging and related uses; campgrounds; airport; public park; public playground; public play field; stadium; armory; auditorium; golf course; fire station; library; museum; military training facility; cemetery; mausoleum; school; educational institution; public school or institution for those with disabilities or special needs; penal institution; reformatory; detention and correction home, institution or school; hospital; public medical and dental clinic; or municipal or governmental service building and use (e.g., reservoir, water tower, pump station, sewage treatment facility, water treatment facility, refuse transfer station or landfill, or caretaker’s unit associated with the primary use). (Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)
2.8.120 Applicability.
The public overlay is available to properties in public, semi-public, or governmental ownership. A zone map amendment (Chapter 4.7 SDC) is required to apply the overlay to properties in public, semi-public, or government ownership that change to a public, semi-public or government use. The overlay zone is in addition to the site’s base zone. Development of site with the (/P) overlay shall be consistent with the comprehensive plan and the public overlay standards as identified below in accordance with Article 4. (Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010; Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)
2.8.130 Abandoning use – Transfer of ownership.
Whenever property within the public overlay (/P) is transferred to private ownership, such transferred area shall have the public overlay removed and the base zoning shall be the applicable zoning district for the property. Future development shall be consistent with the provisions of the applicable base zone and other relevant sections of the development code. (Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)
2.8.140 Changing use.
Any area shown on the official zoning map that has the public overlay (/P) shall be developed in accordance with the provisions of the public overlay zone and in accordance with Article 4. (Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010; Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008)
2.8.150 Allowed uses.
|
Use Categories (Examples of uses are in Chapter 1.6 SDC; definitions are in Chapter 1.5 SDC.) |
Public (P) |
|---|---|
|
Residential Categories |
|
|
All residential uses (household living and group living) allowed, if: |
|
|
- Lawfully existing as of September 1, 2006, or |
P |
|
- Replacement or rebuilding of residential structure conforming to the same footprint as previously existed as of April 5, 2010, or |
P |
|
- New dwelling, freestanding, or |
CU |
|
- New dwelling(s) built in conjunction with a permitted use, including caretaker dwellings |
P |
|
Commercial Categories |
|
|
Drive-up/drive-in/drive-through (drive-up windows, kiosks, ATMs, similar uses/facilities), per SDC 2.3.160(A) |
N |
|
Bed and breakfast inn, per SDC 2.2.200 |
N |
|
Educational services, not a school (e.g., tutoring or similar services) |
P |
|
Entertainment, major event |
P |
|
Mobile food vendor, per SDC 2.3.160(B) |
S |
|
Offices |
P |
|
Outdoor recreation, commercial |
P |
|
Parking lot (when not an accessory use) |
P |
|
Quick vehicle servicing or vehicle repair. (See also drive-up/drive-in/drive-through uses, per SDC 2.3.160) |
|
|
- Fully enclosed (e.g., garage) |
N |
|
- Not enclosed |
N |
|
Retail sales and service (see also drive-up uses, per SDC 2.3.160) |
|
|
- Fully enclosed (e.g., garage) |
N |
|
- Not enclosed (other than accessory uses) |
N |
|
- Eating establishments as an accessory use, enclosed in same building with primary use |
P |
|
- Eating establishment not enclosed |
N |
|
Self-service storage |
N |
|
Industrial Categories |
|
|
Industrial service (see also drive-up uses) |
|
|
- Fully enclosed (e.g., office) |
N |
|
- Not enclosed |
N |
|
Manufacturing and production |
|
|
- Fully enclosed |
N |
|
- Not enclosed |
N |
|
Warehouse and freight movement |
N |
|
Waste-related |
CU |
|
Wholesale sales |
|
|
- Fully enclosed |
N |
|
- Not enclosed |
N |
|
Institutional Categories |
|
|
Basic utilities |
P |
|
Renewable energy facilities |
|
|
- Accessory use |
CU+S |
|
- Primary use |
CU+S |
|
Nonrenewable energy facilities |
N |
|
Cemeteries, mausoleums, crematoriums, funeral services |
CU |
|
Colleges |
CU |
|
Community service |
P |
|
Daycare, adult or child daycare; does not include family daycare (16 or fewer children) under ORS 657A.250 |
P |
|
Parks and open space |
P |
|
Religious institutions and houses of worship |
CU |
|
- Transitional shelter communities, per the standards in SDC 2.2.200(N) |
CU |
|
Schools |
|
|
- 20 or fewer students |
P |
|
- More than 20 students |
CU |
|
Wildlife rehabilitation facility |
CU |
|
Other Categories |
|
|
Accessory structures (with a primary permitted use) |
P |
|
Agriculture – animals |
N |
|
Agriculture – nurseries and similar horticulture (see also, wholesale and retail uses) |
CU |
|
Historic building alterations, per Chapter 3.5 SDC |
S |
|
Mining |
N |
|
Radio frequency transmission facilities and telecommunication towers and antennas, except those allowed as ancillary to a primary permitted use |
CU |
|
Rail lines and utility corridors, except existing facilities on nonzoned RR properties are permitted |
CU |
|
Temporary uses (limited to P and CU uses), per SDC 4.9.100 |
P/CU |
|
Transportation facilities (operation, maintenance, preservation, and construction in accordance with the city’s transportation system plan) |
P |
|
Jails and detention facilities |
CU |
|
Key: P = Permitted, subject to land use review or design review (Chapter 4.2 SDC). Other uses may be allowed with a planned development. S = Permitted with standards (SDC 2.3.160). Other uses may be allowed with a planned development. CU = Conditional use required (Chapter 4.4 SDC). Other uses may be allowed with a planned development. N = Not permitted. |
|
(Ord. 18-22 § 3, 2018; Ord. 14-01 § 1 (Exh. A), 2014; Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010)
2.8.160 Public overlay district standards.
A. Land Development.
|
All Main Buildings Including Dwellings |
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Cemeteries, Educational Facilities, and Park Districts |
Amusement, Recreation, Hospital, and Service Districts |
|
Maximum number of main buildings per lot |
Not limited |
Not limited |
|
Minimum Lot Area: |
|
|
|
Dwellings – Same as prescribed for dwellings in |
RM-10 district |
RM-10 district |
|
Minimum lot width |
Not limited |
Not limited |
|
Maximum lot coverage |
30 percent |
Not limited |
|
Maximum height |
2.5 stories or 35 feet |
6 stories or 70 feet |
B. Yards.
1. The setbacks for the public overlay shall be the same as the underlying zoning district of the property.
2. Special Setbacks. Particular segments of arterial streets have been designated with special setback lines to provide better amenities along such streets. When a yard abuts such a street, the yard depth will be measured from the special setback line. See the official zoning map for the streets which have a special setback.
C. Building Orientation Standards. Developments subject to this section shall have their buildings oriented to a street, as generally shown in Figure 2.8.160(C)(1). All of the following criteria must be met:
1. Compliance with the setback and build-to line standards, where applicable in the underlying zone. The build-to line may be set back to provide additional space for pedestrian amenities between a building and its adjoining street. In the DC underlying zone, the maximum setback is five feet.
2. Except as provided in subsections (C)(4) and (5) of this section, all buildings shall have at least one primary building entrance (i.e., dwelling entrance, a tenant entrance, lobby entrance, or breezeway/courtyard entrance) facing an adjoining street (i.e., within 45 degrees of the street property line), or if the building entrance is turned more than 45 degrees from the street (i.e., front door is on a side elevation), the primary entrance shall not be more than 60 feet in the GC underlying zone, except to provide pedestrian amenities; a walkway shall connect the primary entrance to the sidewalk. In the DCF underlying zone, all buildings with street frontage must have at least one primary building entrance facing an adjoining street. Additionally, street-facing facades of buildings shall provide an entrance at least every 45 feet along the street.
3. Off-street parking, driveways, and other vehicle areas shall not be placed between buildings and the street(s) to which they are oriented. Off-street parking shall be oriented internally to the site, with parking bays separated by landscaping, as generally shown in Figure 2.8.160(C)(1). Bays shall contain no more than 10 parking spots each, as an average over all contiguous parking bays on the same parcel.
Figure 2.8.160(C)(1) - Building Orientation with Internal Parking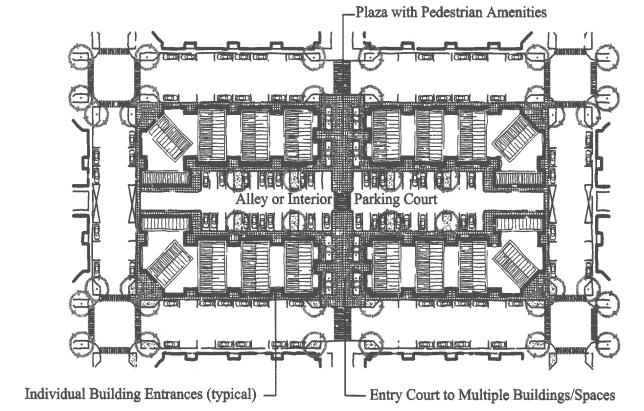
4. The building orientation standard may be met with vehicle areas allowed between the street right-of-way and a building’s primary entrance when the approval body finds that all of the following criteria are met:
a. Placing vehicle areas between the street right-of-way and building’s primary entrance will not adversely affect pedestrian safety, comfort or convenience, based on the distance from the street sidewalk to the building entrance, projected vehicle traffic volumes, and available pedestrian walkways;
b. The proposed vehicle areas are limited to one drive aisle of not more than 20 feet in width with adjoining bays of not more than eight consecutive parking spaces per bay (including ADA accessible spaces) on the side(s) of the drive aisle. (The intent of which is to create a drive aisle that is street-like, and to break up parking into small bays with landscaping.); and
c. The building’s primary entrance is connected to an adjoining street by a pedestrian crosswalk as specified under SDC 3.1.300.
5. Where a development contains multiple buildings and there is insufficient street frontage to which buildings can be oriented, a primary entrance may be oriented to plaza or courtyard. When oriented in this way, the primary entrance(s) plaza or courtyard shall be connected to the street by a pedestrian walkway meeting the standards in SDC 3.1.300. (Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010; Ord. 08-06 § 3, 2008. Formerly 2.8.150)
2.8.170 Public overlay design standards.
A. Purpose. This section promotes the public health, safety, and welfare by requiring at least a minimum level of design on every building in the public overlay district. Design is important to identifying Silverton as a unique place with successful public use areas. The design standards are intended to:
1. Encourage architecture that is consistent with the character of Silverton.
2. Ensure that new development creates a close, intimate human scale and architectural designs address all four sides of a building.
3. Encourage the use of contextually appropriate materials, textures and colors.
4. Promote pedestrian-oriented uses by orienting buildings and their entrances to the street or to civic spaces abutting the street.
5. Create vibrant civic spaces (e.g., plazas, public art, cafe seating areas, etc.) oriented to take advantage of southern exposures; civic spaces should help identify the village, create intrigue, and offer weather protection and comfort to pedestrians while adding value to adjoining properties.
6. Break down large building masses and provide visual interest along the street.
7. Balance rhythm and continuity – encourage creativity in the design of building elevations, rooflines and facade elements.
8. Treat corner lots as focal points with vertical elements, public art, seating, and other design features.
9. Provide weather protection where commercial and mixed-use buildings abut the street.
B. Applicability. The following standards are applied through design review prior to building permit review. The applicant is required to demonstrate that the standards are met by complying with the criteria under each standard. Remodels of, or additions to, designated historic residential structures are subject to the requirements under Chapter 3.5 SDC. The provisions of this section may be adjusted through the design performance option in SDC 4.2.510.
C. Pedestrian Orientation. The design of all buildings on a site shall support a safe and attractive pedestrian environment. This standard is met when the approval body finds that all of the criteria in subsections (C)(1) through (8) of this section are met. Alternatively, the approval body may approve an alternate design under SDC 4.2.510 through a Type III procedure upon finding that the proposed design equally or better achieves the above standard.
1. The building orientation standards under SDC 2.8.160 are met;
2. Primary building entrances shall open directly to the outside and, if not abutting a street, shall have walkways connecting them to the street sidewalk; every building shall have at least one primary entrance that does not require passage through a parking lot or garage to gain access;
3. Corner buildings (i.e., buildings within 20 feet of a corner as defined by the intersecting curbs) shall have corner entrances, or shall provide at least one entrance within 20 feet of the street corner or corner plaza;
4. At least 50 percent of a building’s street-facing elevation(s) shall be located at the build-to line or closer to the street; build-to lines are prescribed by SDC 2.8.150;
5. Ground floor windows or window displays shall be provided along at least 50 percent of the building’s (ground floor) street-facing elevation(s). Design elements such as large regularly spaced and similarly shaped windows with window trim, and with transom or clerestory windows above building entrances are counted; windows and display boxes shall be integral to the building design and not mounted to an exterior wall;
6. Windows shall cover no more than 90 percent of the ground floor facade length, and shall not begin less than 18 inches or more than 30 inches above the sidewalk (except transom windows). Second and third story windows shall match the vertical and horizontal character of ground level windows;
7. Street-facing elevations shall be designed with weather protection, such as awnings, canopies, overhangs, or similar features. Such weather protection shall project a minimum of four feet and a maximum of eight feet over sidewalks or other pedestrian space;
8. Drive-up and drive-through facilities, when allowed, shall conform to SDC 2.3.160.
D. Compatibility. All new buildings and major remodels shall be designed consistent with the architectural context in which they are located. This standard is met when the approval body finds that all of the criteria in subsections (D)(1) through (6) of this section are met. Alternatively, the applicant may propose different design elements as provided under SDC 4.2.510, Design performance option.
1. There is continuity or effective transitions in building sizes between new and existing buildings;
2. The ground floor and upper floor elevations and architectural detailing are compatible with adjacent buildings;
3. Roof elevation is compatible with adjacent buildings (roof pitch, shape, height step-down);
4. There is continuity in the rhythm of windows and doors on the proposed building(s);
5. The relationship of buildings to public spaces, such as streets, plazas, other areas, and public parking, including on-street parking, is strengthened by the proposed building(s);
6. The materials, colors, and architectural style are compatible with Silverton’s character. Compatible materials include masonry, tile, stucco, split face concrete blocks, or wood. Unadorned poured or tilt-up concrete or metal siding are subject to design review. Entirely pre-cast concrete buildings are not permitted. Where blank walls are required for structural reasons, all such walls visible from public streets shall include a combination of architectural elements and features such as offsets, entry treatments, patterns of varied materials and colors, decorative murals and divisions into bays, or similar features.
E. Human Scale. The design of all buildings shall be to a human scale. This standard is met when the approval body finds that all of the criteria in subsections (E)(1) through (9) of this section are met. Alternatively, the applicant may propose different design elements as provided under SDC 4.2.510, Design performance option.
1. Regularly spaced and similarly shaped windows are provided on all building stories;
2. Ground floor spaces have tall ceilings (i.e., 12 through 16 feet) with display windows on the ground floor;
3. Display windows are trimmed, recessed, or otherwise defined by wainscoting, sills, water tables, or similar architectural features;
4. On multistory buildings, ground floors are defined and separated from upper stories by appropriate architectural features (e.g., cornices, trim, awnings, canopies, arbors, trellises, overhangs, or other features) that visually identify the transition from ground floor to upper story; such features should be compatible with the surrounding architecture;
5. The tops of flat roofs are treated with appropriate detailing (i.e., cornice, pediment, flashing, trim, or other detailing) that is compatible with the surrounding architecture;
6. Pitched roofs have eaves, brackets, gables with decorative vents, or other detailing that is consistent with the surrounding architecture;
7. Historic design and compatibility requirements under Chapter 3.5 SDC, where applicable, are met;
8. Where buildings with greater than 10,000 square feet of enclosed ground floor space are proposed, they shall provide articulated facades on all street-facing elevations. This criterion is met when there is a major break in the building plane not less than once for every 30 feet of a building’s horizontal length. Breaks in building plane include windows, primary entrances, weather protection (awnings, canopies, arbors, arcades), offsets/projections/changes in elevation or horizontal direction, sheltering roofs, terraces, a distinct pattern of divisions in surface materials, ornamentation, screening trees, small-scale lighting (e.g., wall-mounted lighting or up-lighting), and/or similar features as generally shown in Figure 2.3.180(E). See also subsection (C) of this section; and
9. Utility equipment within landscaped areas or attached to structures are screened from view from public rights-of-way. (Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010)
2.8.180 Special use standards.
A. Renewable Energy Facilities. Where renewable energy facilities are allowed, they shall require approval through conditional use review (Type III) and conform to all of the following standards.
1. Primary or Accessory Use. The use may be primary or accessory to an allowed use within the public overlay.
2. Maximum Height and Setback. Renewable energy facilities structures built according to the International Building Code shall meet the maximum height and setback standards of SDC 2.4.150(A).
3. Performance Standards. Renewable energy facilities shall not exceed the performance standards stated by SDC 2.4.170(C).
4. Landscaping. Screening and buffering for the facilities within the public overlay shall follow the standards of SDC 3.2.300.
5. Other Permit or Licensing Requirements. The owner of the facility shall be responsible for obtaining and complying with all other applicable permit and/or licensing requirements. (Ord. 10-02 Exh. A § B, 2010)


