Chapter 1.3 –
Definitions
Sections:
1.3.100 Meaning of Words Generally
1.3.200 Meaning of Common Words
1.3.300 Meaning of Specific Words and Terms
1.3.100 Meaning of Words Generally
All of the terms used in this Development Code have their commonly accepted, dictionary meaning unless they are specifically defined in this chapter or the context in which they are used clearly indicates to the contrary. Webster’s Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged, shall be considered the standard reference. [Ord. 497 § 2 (Exh. B), 2019].
1.3.200 Meaning of Common Words
Tense – All words used in the present tense include the future tense.
Singular/plural – All words used in the singular include the plural, and all words used in the plural include the singular unless the context indicates to the contrary.
Use of “shall,” “will,” “should” and “may” – The words “shall” and “will” are mandatory and the words “should,” and “may” are permissive.
Use of “land,” “property,” “lot” and “parcel” – The words “land,” “property,” “lot” and “parcel” are used interchangeably unless the context clearly indicates to the contrary.
1.3.300 Meaning of Specific Words and Terms
As used in this Code, the following words and phrases mean:
A
Abutting – Two or more lots or features (such as buildings) joined by a common boundary line or point. It shall include the terms adjacent, adjoining and contiguous.
Access – A way or means by which pedestrians, bicycles and vehicles enter or leave property.
Access easement – An easement recorded for the purpose of providing vehicle, bicycle, and/or pedestrian access from a public street to a parcel across intervening property under separate ownership from the parcel being provided access.
Access management – The control of street (or highway) access for the purpose of improving the efficiency, safety and/or operation of the roadway for vehicles; may include prohibiting, closing, or limiting direct vehicle access to a roadway from abutting properties, either with physical barriers (curbs, medians, etc.) or by land dedication or easement.
Access Point – Any driveway, street, turnout or other means of providing for the movement of vehicles to or from the public roadway system.
Accessible – Any physical feature, structure or improvement that is approachable and usable by people with physical disabilities, consistent with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Accessory building or structure – A building or structure of secondary importance or function on a site. In general, the primary use of the site is not carried on in an accessory structure. Accessory structures may be attached or detached from the primary structure. Examples of accessory structures include: garages, sheds, workshops, greenhouses, guest houses and similar structures.
Accessory dwelling – see Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Accessory use – A use or activity which is a subordinate part of a primary use and which is clearly incidental to a primary use on a site.
Adjacent – See Abutting.
Administrative – See Land Use Decision Types.
Adult business/Adult entertainment – Any business activity or establishment involving the display or exhibition of live or reproduced materials which has an emphasis on nudity, and/or sexual activity, and which limit their patrons to persons of at least 18 years of age.
Adverse Impact – Negative effect of development that can be measured, including but not limited to excessive traffic, noise, air pollution, vibration, light, odors, density, massing, and dust.
Affordable housing unit – Housing reserved for occupancy by eligible households and affordable to households whose annual income does not exceed 80 percent of area median income, adjusted for household size, and no more than 30 percent of the monthly household income is paid for monthly housing expenses. (Housing expenses for ownership housing include mortgage and mortgage insurance, property taxes, property insurance, and homeowner dues. Housing expenses for rental housing include rent and appropriate utility allowance.)
Agency – For the purposes of its use in the Development Code, the term Agency collectively refers to the City of Sisters Community Development Department, Public Works Department, City Engineer, Sisters-Camp Sherman Fire Protection District and other state or federal regulatory authorities such as but not limited to the Oregon Department of Transportation, Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, Oregon Department of Emergency Management, United States Corps of Engineers and the United States Forest Service.
Agriculture – As used in this Code, “agriculture” is the same as “farm use.” See also ORS 215.203.
Alley – See Street/Road Related Definitions.
Ambient – Something that surrounds, as in the level of light, dust or noise.
Amusement use – A building or site that provides a means of entertainment that is not otherwise defined (arcade, bowling alley, billiard parlor, etc).
Animal Hospital – A place where animals or pets are given medical or surgical treatments and are cared for during the time of such treatment. Use as a kennel shall be limited to short-time boarding and shall be limited to be incidental to such hospital use.
Antenna means any system of wires, poles, rods, reflecting discs or similar devices designed for telephonic, radio, facsimile, data, or television communications through sending and/or receiving of electromagnetic waves when such system is either external to or attached to the exterior of a structure. Antennas shall include, but not be limited to, devices having active elements extending in any direction, and directional beam-type arrays having elements carried by and disposed from a generally horizontal boom that may be mounted up and rotated through a vertical mast or tower interconnecting the boom and antenna support, all of which elements are deemed to be part of the antenna.
Antenna height means the vertical distance measured from the ground surface at grade to the tip of the highest point of the antenna on the proposed structure.
Applicant – A person who applies for a land use review or building permit. An applicant can be the owner of the property or an authorized agent of the property owner, such as a builder, developer, consultant, or architect.
Arterial – See Street/Road Related Definitions.
Articulate/articulation – The joining and interrelating of building spaces through offsets, projections, overhangs, extensions and similar features.
Assembly, Club – An organization of people who voluntarily meet on a regular basis for a mutual purpose.
Assisted Living Facility – A facility that provides a “social model of care”, designed to meet the social needs as well as the medical needs of people requiring placement in a supervised care facility. Costs for care are flexible, depending on the level of care necessary for individuals to maintain their independence. Assisted living facilities are considered a type of residential care facility, see also residential care facility.
Attached dwelling/townhome – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Auto-dependent use – The use services motor vehicles and would not exist without them, such as vehicle repair, gas station, quick lube/service facilities, car wash, auto and truck sales.
B
Base station means a structure or equipment at a fixed location that enables Federal Communications Commission (FCC) licensed or authorized wireless communications between user equipment and a communications network. The term does not encompass a tower as defined in this section or any equipment associated with a tower.
1. The term includes, but is not limited to, equipment associated with wireless communications services such as private, broadcast, and public safety services, as well as unlicensed wireless services and fixed wireless services such as microwave backhaul.
2. The term includes, but is not limited to, radio transceivers, antennas, coaxial or fiberoptic cable, regular and backup power supplies, and comparable equipment, regardless of technological configuration (including distributed antenna systems and small-cell networks).
3. The term includes any structure other than a tower that supports or houses equipment described in subsections 1. and 2. of this definition that has been reviewed and approved under the applicable zoning or siting process, or under another State or local regulatory review process, even if the structure was not built for the sole or primary purpose of providing such support.
4. The term does not include any structure that does not support or house equipment described in subsections 1. and 2. of this definition.
Bed and breakfast inn – Generally owner-occupied dwelling with guest rooms, plus guest common areas separate from the owner’s quarters. Breakfast is the only meal served, to overnight guests only. Located in a legally zoned area, and complies with all local tax, fire, building and health requirements.
Berm – Mounded or elongated landscape hills constructed for many reasons such as blocking out unwanted or unsightly views, directing or redirecting foot traffic or drainage, creating subtle and natural-looking privacy, adding raised elements to the garden, or simply emphasizing a particular area or focal point.
Beveled building corner – A rounded or flat edge on a building, usually at a street corner; may include an entrance, windows, pillars or other architectural details and ornamentation.
Bicycle – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Bicycle facilities – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Bicycle, pedestrian and non-motorized related definitions:
|
• |
Bicycle – A vehicle designed to operate on the ground on wheels, propelled solely by human power, upon which any person or persons may ride with wheels at least 4 inches in diameter. |
|
• |
Bicycle facilities – A general term describing improvements and provisions made to accommodate or encourage bicycling, including bicycle parking facilities (i.e. racks and lockers) and bikeways. |
|
• |
Bikeway – Any road, path, or way that is specifically open to bicycle travel, regardless of whether such facilities are designated for the exclusive use of bicycles or are shared with other transportation modes. The two types of bikeways are: |
o Bike lane – A portion of the roadway that has been designated by permanent striping and pavement markings or signage for the exclusive use of bicycles.
o Shoulder bikeway – The paved shoulder of a roadway that is 4 feet or wider; typically shared with pedestrians in areas without curbs and sidewalks.
|
• |
Multi-Use related definitions: |
o Multi-use path – A paved access way that accommodates bicycles and other non-motorized users; typically shared with pedestrians.
o Multi-use trail – An unpaved path that accommodates all-terrain bicycles and other non-motorized users; typically shared with pedestrians.
|
• |
Pedestrian/Non-motorized related definitions: |
o Pathway – An at-grade paved path that is generally separated from the roadway by a planter strip or drainage swale.
o Sidewalk – A paved walkway that is generally located adjacent to and separated from a street/road by a curb or curb and planter strip.
|
• |
Pedestrian amenities – Pedestrian areas and objects that serve for socializing, gathering, resting and enjoyment of the City’s commercial areas and contribute to a walkable district. |
|
• |
Pedestrian facilities – A general term denoting improvements and provisions made to accommodate or encourage walking, including sidewalks, crosswalks, ramps, pathways and trails. |
|
• |
Pedestrian-oriented development – Development which is designed to maximize pedestrian access to the site and building, rather than auto access and parking areas. The building’s main entrance is oriented to the street sidewalk. |
Bike lane – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Block – A parcel of land or group of lots bounded by intersecting grid streets.
Bollard – A post of metal, wood or masonry that is used to separate or direct traffic (vehicles, pedestrians and/or bicycles). Bollards are usually decorative, and may contain sidewalk or pathway lighting.
Boulevard – A street with broad open space areas, typically with planted medians.
Broadcast communication facility means any facility that transmits radio or television signals including, but not limited to, antennas, dish antennas, microwave antennas, and other types of equipment for the transmission of such signals, including towers and similar supporting structures, equipment cabinets or buildings, parking areas, and other accessory development. This definition does not apply to amateur radio stations as defined by the Federal Communications Commission, Part 97 of the Commission’s Rules.
Building-related definitions:
|
• |
Building – Any structure used or intended for supporting or sheltering any use or occupancy. |
|
• |
Elevation – Refers to a building facade, or scaled drawing of the same, from grade to the highest point on the structure. |
|
• |
Envelope – The three dimensional space which is to be occupied by a building. |
|
• |
Facade – The exterior walls of a building exposed to public view. |
|
• |
Footprint – The outline of a building as measured around its exposed foundation. |
|
• |
Frontage – A lineal front footage of a building or portion thereof devoted to a specific business or enterprise. |
|
• |
Height – The vertical distance measured between the highest point of the roof and the nearest average finished grade. |
|
• |
Mass – The volume of a building, or the total height, width, and depth of all its parts. |
|
• |
Orientation – The positioning of a building or a focal point of a building (such as an entrance) toward a particular point of reference (e.g., “the front facade of the building is oriented to the street”). |
|
• |
Pad – A vacant building site on a lot with other building sites. |
|
• |
Ridge line – The top of a roof at its highest point above the finished grade. |
|
• |
Roof line – The line which marks the highest point of the vertical front of a building in the case of a false front, or the line where the roof is joined to the vertical front wall of the building in other cases. |
|
• |
Roof pitch – The slope of a roof, usually described as a ratio of rise to run. |
|
• |
Scale – The dimensional relationship of a building and its component parts to other buildings. |
Bulkhead – The wall below ground-floor windows on a building (i.e., may be differentiated from other walls by using different materials or detailing).
Business – A commercial or industrial enterprise or establishment.
Business Premises – A parcel of property or that portion thereof occupied by one tenant.
C
Camouflaged means any wireless or broadcast communication facility that is designed to blend into the surrounding environment. Examples of camouflaged facilities may include architecturally screened roof-mounted antennas, building-mounted antennas painted to match the existing structure, antennas integrated into architectural elements, towers made to look like trees and antenna support structures designed to look like flag poles or light poles.
Canopy – A permanent roofed structure which may be free-standing or partially attached to a building for the purpose of providing shelter to patrons in automobiles, and patrons on foot, but shall not mean a completely enclosed structure.
Capacity – Maximum holding or serviceability, as used for transportation, utilities, parks and other public facilities.
Caretaker’s Unit – A caretaker unit is a separate dwelling unit that is accessory to a principal non-residential use and situated on the same parcel.
Carport – A stationary structure consisting of a roof, and its supports, not fully enclosed, and used to shelter motor vehicles, recreational vehicles, or boats.
Carport, portable – A portable and relocateable as opposed to permanently built accessory structure, for the storage of automobiles, boats or trailers.
Centerline radius – The radius of a centerline of a street right-of-way.
Child Care Center (commercial) – Any registered or certified child care facility which is not a family child care home.
Child Care Home (residential) – Any registered or certified family child care home where child care is offered to for no more than 16 children, including children of the provider, regardless of full-time or part-time status (ORS 657A.).
Clear and objective – Relates to decision criteria that do not involve substantial discretion or individual judgment in their application.
Co-location means locating wireless or broadcast communication equipment from more than one provider on a single support structure.
Collector – See Street/Road Related Definitions.
College or university – a place of higher education.
Commercial – Land use involving buying/selling of goods or services as the primary activity.
Common area – Land commonly owned to include open space, landscaping, recreation, parking, or access facilities and available for public use or use by all property owners association members and guests.
Community Center – A meeting place, often a complex of buildings, where people may carry on cultural, recreational, or social activities.
Community Development Director – The director of the City’s Community Development Department or his or her designee. For the purposes of this code, the terms “Development Services Director” and “Planning Director” shall be interchangeable.
Comprehensive Plan – The plan adopted by the City of Sisters pursuant to ORS 197 and 215 in compliance with the Statewide Planning Goals. The Comprehensive Plan is an expression of public policy and it provides the basis for implementation through this Development Code.
Concert Hall – An area where concerts are given; a room or area for gatherings or entertainment.
Conditional use – A use that may be allowed, if it meets prescribed conditions in the Development Code or additional conditions as set forth by the decision-making body. A Minor Conditional Use Permit is processed as a Type II procedure and a Conditional Use Permit is processed as a Type III procedure.
Conservation easement – An easement that protects identified natural features of the land, such as wetlands, woodlands, significant trees, floodplains, wildlife habitat, and similar resources.
Convenience Market – A store selling a limited variety of basic items including prepackaged foods, snack foods, beverages and nonfood products. Also known as a mini-mart.
Corner clearance – The distance from an intersection of a public or private street to the nearest driveway or other access connection, measured from the closest edge of the pavement of the intersecting street to the closest edge of the pavement of the connection along the traveled way.
Corner lot – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Corner radius – The radius of a street corner, as measured around the curb or edge of pavement.
Cornice – The projecting horizontal element that tops a wall or flat roof.
Cottage – A small house that may be used as an accessory dwelling.
Cottage development – Means a grouping of cottages developed as part of a Master Planned Development, with a minimum of four cottages.
Courtyard – A court or enclosure adjacent to a building which usually includes amenities such as gardens, planters, seating, or art.
Criteria – Criteria are the elements required to comply with a particular standard.
Cross Access – A service drive providing vehicular access between two or more contiguous sites so the driver need not enter the public street system.
Cul-de-sac – A dead end street intended for local traffic that typically terminates with a bulb or other vehicle turnaround.
Curb cut – A driveway opening where a curb is provided along a street.
D
Data Center – Data storage and processing facilities, electronic products – manufacture, storage and assembly, together with all related and supporting uses and facilities.
Deciduous – Tree or shrub that sheds its leaves seasonally.
Decorative Lighting – Festoon type lights, limited to small individual low wattage bulbs on a string.
Dedication – The conveyance of land by its owner for any public use as shown on an approved plat, map or deed. Dedication does not include reservations or easements.
Density – A measurement of the number of dwelling units in relationship to a specified amount of land. As used in this Code, density is determined based on the gross parcel or lot area and includes all buildable and unbuildable land such as streets, streams, slopes, open space, easements, other rights-of-ways and land that will be dedicated as right-of-way through the development process. It does not include land previously dedicated as right-of-way.
Developable – Buildable land, as identified by the City’s Comprehensive Plan. Includes both vacant land and land likely to be redeveloped, per ORS 197.
Developed open space – See Open Space Definitions.
Development – All improvements on a site, including buildings, other structures, parking and loading areas, landscaping, paved or graveled areas, grading, and areas devoted to exterior display, storage, or activities. Development includes improved open areas such as plazas and walkways, but does not include natural geologic forms or landscapes.
Diameter at Breast Height (DBH) – Tree diameter at breast height. Breast height is defined as 4.5 feet above the ground on the uphill side of the tree.
Discontinued/abandoned use – A use that physically vacates the land it was on for a period of one calendar year or longer, cessation of an allowed activity, or use terminated at the end of any lease or contract.
Discretionary – Describes a permit action or decision that involves substantial judgment or discretion.
Drip-line – Imaginary line around the eave of a structure, or a tree or shrub at a distance from the trunk equivalent to the canopy (leaf and branch) spread.
Drive lane/travel lane – A paved driving surface for one lane of vehicles.
Drive-through facility – A facility or structure that is designed to allow patrons to remain in their vehicles while services and/or goods are being provided on the site. Drive-through facilities also include facilities designed for the rapid servicing of vehicles, where the drivers may or may not remain in their vehicles, but where the drivers either perform the service for themselves, or wait on the site for the service to be rendered. Examples include but are not limited to drive-up windows for banks, restaurants, coffee kiosks and similar vendors; gas pump islands; car wash facilities; auto service facilities such as quick-lube or quick-oil change facilities; and drive-in theaters.
Driveway – Areas that provide vehicular access to a site, except for public and private streets. A driveway begins at the property line and extends into the site. Driveways do not include parking spaces, maneuvering, or circulation areas in parking lots.
Driveway apron/approach – The edge of a driveway where it abuts a public way, usually constructed of concrete.
Drought Tolerant – Vegetation which is adapted to dry, arid or drought conditions.
Duplex – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Dwelling-related definitions:
|
• |
Accessory dwelling – A second dwelling unit on a lot or parcel with a single-family unit as a primary use that contains one or more rooms with private bath and kitchen facilities comprising an independent, self-contained dwelling unit. |
|
• |
Duplex dwelling – A building with two attached housing units on one lot or parcel. The units must share a common wall or common floor/ceiling. |
|
• |
Dwelling unit – A single unit, providing complete, independent living facilities for one or more persons, including permanent provisions for living, sleeping, eating, cooking and sanitation and that is lawfully connected to the City’s municipal water and sewage disposal systems unless exempt as provided by SMC 13.40. |
|
• |
Fourplex dwelling – Means a single building on its own lot with four dwelling units. |
|
• |
Manufactured dwelling – A residential trailer, mobile home or manufactured home each as defined in ORS Chapter 446. Manufactured dwelling does not include any building or structure constructed to conform to the State of Oregon Structural Specialty Code or the Low-Rise Residential Dwelling Code or any unit identified as a recreational vehicle by the manufacturer. |
|
• |
Multi-family development – Residential development that provides four or more dwellings on an individual lot or parcel (e.g., multi-family dwellings, multi-plexes, apartments, condominiums, etc.). |
|
• |
Single family attached dwelling, townhome – Single family dwellings on their own lots or parcels, sharing a common side wall at the property line. |
|
• |
Single family detached dwelling – One dwelling unit, freestanding and structurally separated from any other building, located on a lot. |
|
• |
Triplex dwelling – A building with three attached housing units on one lot or parcel. |
|
• |
Work/live townhome – A residential townhome unit in which a business shall be operated. |
|
• |
Zero-lot line dwelling – Detached single family dwelling that is not subject to side yard setbacks on one side of a lot. |
E
Easement – A grant of one or more of the property rights by the property owner to and/or for use by the public, a corporation or another person or entity.
Eave – Lowest horizontal line of a roof.
Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations – Designated areas containing external chargers for electric vehicles. Each station contains a plug that becomes attached to the vehicle, providing it with a current of electrical energy needed for propulsion.
Elevation – See Building-Related Definitions.
Equipment building, shelter or cabinet means a cabinet or building used to house equipment used by wireless or broadcast communication providers at a facility.
Event – A gathering that may include a ceremony, competition, convention, festival, party or sporting event that is not accessory to the primary use.
Evidence – Application materials, plans, data, testimony and other factual information used to demonstrate compliance or non-compliance with a code standard or criterion.
F
Facade – See Building-Related Definitions.
Fire apparatus lane – Unobstructed area or driveway meeting applicable Fire Code requirements; typically may not be used for parking or loading area.
Flag lot – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Flood-related definitions:
|
• |
Area of special flood hazard – The land in the flood plain within a community subject to a 1 percent or greater chance of flooding in any given year. The area may be designated as Zone A on the Flood Insurance Rate Maps. Zone A may be refined into Zones A, AO, AH, A1-30, AE, A99, AR, AR/A1-30, AR/AE, AR/AO, AR/AH, AR/A, VO, or V1-30, VE, or V. For purposes of these regulations, the term “special flood hazard area” is synonymous in meaning with the phrase “area of special flood hazard.” |
|
• |
Base flood – The flood having a one percent chance of being equaled or exceeded in any given year. Base flood is the same as the “100-year flood.” |
|
• |
Basement – Any area of the building having its floor subgrade (below ground level) on all sides. |
|
• |
Development – Any man-made change to improved or unimproved real estate, including but not limited to buildings or other structures, mining, dredging, filling, grading, paving, excavation or drilling operations or storage of equipment or materials. |
|
• |
Elevated building – A nonbasement building which has its lowest elevated floor raised above ground level by foundation walls, shear walls, posts, piers, pilings, or columns. |
|
• |
Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM) – An official map of a community on which the Administrator has delineated both the special hazard areas and the risk premium zones applicable to the community. |
|
• |
Floodplain – Any land area susceptible to being inundated by water from any source. |
|
• |
Floodway – See regulatory floodway. |
|
• |
Lowest floor – The lowest floor of the lowest enclosed area (including basement). An unfinished or flood resistant enclosure, usable solely for parking of vehicles, building access or storage in an area other than a basement area is not considered a building’s lowest floor; provided, that such enclosure is not built so as to render the structure in violation of the applicable non-elevation design requirements of CFR 60.3. |
|
• |
Regulatory floodway – The channel of a river or other watercourse and the adjacent land areas that must be reserved in order to discharge the base flood without cumulatively increasing the water surface elevation more than a designated height. This term is the same as “floodway.” |
|
• |
Squaw Creek – See Whychus Creek. |
|
• |
Whychus Creek – The creek running through the City of Sisters, originating in the Three Sisters Wilderness and terminating in the Deschutes River above Lake Billy Chinook. FEMA flood studies identify this feature as Squaw Creek, but the name of the creek was officially changed to Whychus Creek in 2005. |
Floor area ratio – The gross floor area of a building on a lot divided by the lot area (in square footage).
Formula Food Establishment – An eating or drinking establishment that: (a) is required by contractual or other arrangements to offer standardized menus, ingredients, food preparation, employee uniforms, interior decor, signage or exterior design; or (b) adopts a name, appearance or food presentation format that causes it to be substantially identical to thirteen or more other establishments regardless of ownership or location.
Fourplex dwelling – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Front lot line – See Lot Line Definitions.
Frontage – The portion of a development site which abuts a public or private street.
Frontage street or road – See Street/Road Related Definitions.
Functional classification – The classification given to streets (such as “alley,” “local,” “collector” or “arterial”) by the City’s Transportation System Plan, or by adopted County or State Transportation System Plans.
G
Garage – A fully enclosed covered structure designed to provide shelter for vehicles, and which is accessory to residential dwellings/units. A garage may be attached to or detached from another structure.
Garage, Parking – A publicly or privately owned structure having one or more tiers of height, used for the parking of automobiles. Public parking garages may include parking spaces for customers, patrons or clients.
Grade – The lowest point of elevation of the finished surface of the ground, paving, or sidewalk within the area between the building and the property line or, when the property line is more than 5 feet from the building, between the building and a line 5 feet from the building. This is the definition used in the Oregon Structural Specialty Code.
Grading – All cuts, fills, embankments, stockpile areas, and equipment maneuvering areas associated with development.
Grocery Store – A store, organized into departments, offering a wide variety of food including meat, produce, dairy, and baked goods along with canned and packaged goods as well as various nonfood items such as household cleaners, pharmacy products, and pet supplies.
Gross acre(s) – The calculation of a subject parcel or lot area that includes all buildable and unbuildable land such as streets, streams, slopes, open space, easements, other rights-of-ways and land that will be dedicated as right-of-way through the development process. It does not include land previously dedicated as right-of-way. (Similar definition: Density).
Gross Floor Area – The total usable floor area in a building, measured to the outside of the exterior walls.
Ground cover – Plant material or non-plant material (e.g., mulch, gravel, bark chips) that is used to cover bare ground.
Guest House – An accessory structure used in conjunction with the main building for temporary housing of non-paying visitors and guests and containing no cooking facilities.
H
Hammerhead turnaround – See Street/Road related definitions.
Hardscape – Hard surface landscape elements, including pathways, decorative pavers, benches, drinking fountains, arbors, pergolas, plazas, and similar amenities.
Height – See Building related definitions.
High visibility means the following types of wireless or broadcast communication facilities:
1. Monopoles, lattice towers and guyed towers.
2. Any wireless or broadcast communication facilities that do not meet the definition of stealth, low visibility, or moderate visibility.
Home occupation – A home occupation is a legal, nonresidential income-producing use or activity that is a secondary use of a residence.
Hostel – Budget oriented, sociable accommodation where guests can rent a bed, usually a bunk bed, in a dormitory and share a bathroom, lounge and sometimes a kitchen. Limited to 25-person occupancy per night excluding manager and/or employees. Rooms can be mixed or single-sex, although private rooms may also be available. Hostels may include a hot meal in the price.
I
Impervious surface – Surface area which does not allow infiltration of water into the ground (e.g., roofs, pavement, etc.).
Improvements – Any man-made physical addition to a property affecting the value or use of that property.
Incidental and subordinate to – A use or portion of a development that is secondary to, and less apparent, than the primary use or other portion of the development.
Infill Development – Development or redevelopment of parcels of land in otherwise built-up areas.
Interior Lot – See Lot related definitions.
K
Kennel – Any premises or building in which four (4) or more dogs or cats or other small animals or any combination thereof at least four (4) months of age are kept commercially for board, breeding, training or sale, except veterinary animal clinics.
L
Land division – The subdividing or partitioning of land for any purpose into lots or parcels, or the creation of lots or parcels for the purpose of sale or lease.
Land use – The main activity that occurs on a piece of land, (e.g., residential, commercial, mixed use, industrial, open space, recreation, street rights-of-way, vacant, etc.).
Land use decision types:
|
• |
Administrative – A discretionary action or permit decision made without a public hearing, but requiring public notice and an opportunity for appeal. |
|
• |
Legislative – A legislative action or decision is the making of law, as opposed to the application of existing law to a particular use (e.g., adoption of, or amendment to, a comprehensive plan or development regulation). |
|
• |
Ministerial – A routine governmental action or decision that involves little or no discretion. The issuance of a building permit is considered a ministerial action. |
|
• |
Quasi-judicial – Refers to an action or decision that requires substantial discretion or judgment in applying the standards or criteria of this Code, and usually involves a public hearing. |
Land use district – As used in this Code, a land use district is the same as a zoning district.
Landscaping – Any combination of living plants such as trees, shrubs, plants, vegetative ground cover or turf grasses, and may include structural features such as walkways, fences, benches, plazas, works of art, reflective pools, fountains or the like. Landscaping also includes irrigation systems, mulches, topsoil, and re-vegetation or the preservation, protection and replacement of existing trees.
Lane, mid-block lane – See Street/Road-Related Definitions.
Legislative – See Land Use Decision Types.
Level of service (LOS) – Level of Service, a range of operating conditions defined for each type of facility and related to the amounts of traffic that can be accommodated at each level.
Livestock – Domestic animal types customarily raised or kept on farms for profit or other purposes. This definition does not include household pets such as dogs and cats.
Local Improvement District (LID) – A public district formed for the purpose of carrying out local improvements (street paving, construction of storm sewers, development of a park, etc.) Property owners within the LID are assessed for the cost of the improvements in accordance with ORS Chapter 223.
Local street – See Street/Road-Related Definitions.
Lot – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Lot area – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Lot coverage – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Lot depth – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Lot width – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Lot-related definitions:
|
• |
Corner lot – A lot situated at the intersection of two streets where the interior angle of such intersection does not exceed 135 degrees. |
|
• |
Flag lot – A lot located behind a frontage lot, plus a strip of land out to the street for an access drive. There are two distinct parts to a flag lot: the “flag” which comprises the actual building site located at the rear portion of the original lot, and the “pole” which provide access from a street to the flag lot. |
|
• |
Interior lot – A lot other than a corner lot and having frontage on only one street. |
|
• |
Lot – A lot is a legally defined piece of land other than a tract that is the result of a land division. This definition includes the State definition of lot (result of subdividing) and parcel (result of partitioning). |
|
• |
Lot area – The total surface area (measured horizontally) within the property lines of a lot. |
|
• |
Lot coverage – The area of a lot covered by a building or buildings and other structures with surfaces more than 30 inches above the finished grade expressed as a percentage of the total lot area. |
|
• |
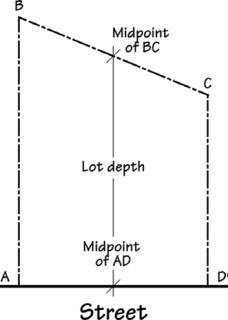
Lot depth – The distance from the midpoint of the front lot line to the midpoint of the rear lot line. |
|
• |
Lot of Record – Lawfully established unit of land means: |
(A) A lot or parcel created pursuant to ORS 92.010 to 92.190; or
(B) Another unit of land created:
(i) In compliance with all applicable planning, zoning and subdivision or partition ordinances and regulations; or
(ii) By deed or land sales contract, if there were no applicable planning, zoning or subdivision or partition ordinances or regulations.
A lawfully established unit of land does not mean a unit of land created solely to establish a separate tax account.
|
• |
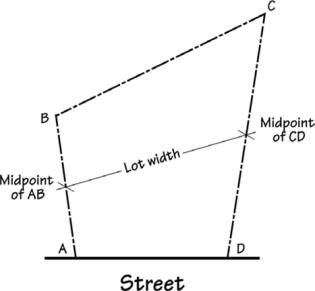
Lot width – The distance from the midpoint of the side lot line to the midpoint of the opposite side lot line. |
|
• |
Parcel – A legally created lot of record, usually created by partitioning of land (ORS Chapter 92). |
|
• |
Through lot – A lot that fronts upon two parallel streets or that fronts upon two streets that do not intersect at the boundaries of the lot. |
Lot Lines – The property lines along the edge of a lot or site:
|
• |
Exterior lot line – Any lot line, other than the front lot line, separating a lot from a street (as in a corner lot). |
|
• |
Front lot line – In the case of an interior lot, a property line which abuts the street; in the case of a corner lot, the applicant can choose which lot line is to be the front lot line and then orient the main entrance to the front lot line. |
|
• |
Rear lot line – The interior lot line opposite and most distant from the front lot line. A triangular lot has two side lot lines but no rear lot line. |
|
• |
Side lot line – Any interior lot boundary that is not a front or rear lot line. |
Lot line adjustment – The adjustment of a common property line where no additional lots are created. This Development Code also defines the consolidation of lots (resulting in fewer lots) as a lot line adjustment.
Low-cost affordable housing unit – Housing reserved for occupancy by eligible households and affordable to households whose annual income does not exceed 50 percent of area median income, adjusted for household size, and no more than 30 percent of the monthly household income is paid for monthly housing expenses. (Housing expenses for ownership housing include mortgage and mortgage insurance, property taxes, property insurance, and homeowners dues. Housing expenses for rental housing include rent and appropriate utility allowance.)
Low-income – a person or household that earns 80 percent or less of the median family income for the area, as published each year by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development.
Low visibility means the following facilities if they do not exceed the height limit of the applicable zoning district, or if they do not increase the height of an existing facility:
1. Whip antennas not exceeding six feet in length or height, including mounting, and measuring no more than three inches in diameter, located on existing structures including, but not limited to, water storage tanks, high-voltage transmission towers, utility towers and poles, sign standards, and roadway overpasses, with equipment cabinets that are screened from view.
2. Facilities, including equipment cabinets, that are screened from view through the use of architectural treatments, such as cupolas, steeples, and parapets, and are consistent with existing development on adjacent properties.
3. Additions to existing permitted low visibility facilities if the additions themselves meet the definition of low visibility and are designed to minimize visibility of both the facility and equipment cabinets.
4. Changes to an existing building that are consistent with the building’s architectural style and the equipment cabinets are not visible.
M
Main/primary entrance – A main entrance is the entrance to a building that most pedestrians are expected to use. Generally, each building has one main entrance. Main entrances are the widest entrance of those provided for use by pedestrians. In multi-tenant buildings, main entrances open directly into the building’s lobby or principal interior ground level circulation space. When a multi-tenant building does not have a lobby or common interior circulation space, each tenant’s outside entrance is a main entrance. Buildings may also have main entrances opening directly into a reception or sales area, a courtyard, or plaza.
Major Retail Development – A major commercial development involves any one or a combination of the following as defined herein:
a. New construction of a commercial development that is greater than twenty thousand (20,000) gross square feet in size; or,
b. New construction of a commercial development on a parcel or combination of parcels comprising five (5) acres or larger; or,
c. Expansion of a commercial development that exists as of the effective date of adoption of this ordinance and which said expansion will increase the square footage of a commercial development to more than twenty thousand (20,000) gross square feet in area or increase the size of the development to more than a total of five (5) acres.
Maneuvering area/aisle – Refers to the driving area in a parking lot where motor vehicles are able to turn around and access parking spaces.
Manufactured dwelling – See Dwelling related definitions.
Manufactured dwelling park – Any place where four or more manufactured dwellings are located within 500 feet of one another on a lot, tract or parcel of land under the same ownership, the primary purpose of which is to rent or lease space or keep space for rent or lease to any person for a charge or fee paid or to be paid for the rental or lease or use of facilities or to offer space free in connection with securing the trade or patronage of such person. ‘Manufactured dwelling park’ does not include a lot or lots located within a subdivision being rented or leased for occupancy by no more than one manufactured dwelling per lot if the subdivision was approved by the local government unit having jurisdiction under an ordinance adopted pursuant to ORS 92.010 to 92.192.
Microcells provide additional coverage and capacity where there are high numbers of users within urban and suburban macrocells. The antennas for microcells are mounted at street level, typically on the external walls of existing structures, lamp-posts, and other street furniture. Microcell antennas are usually smaller than macrocell antennas, and, when mounted on existing structures, can often blend into building features. Microcells provide radio coverage over distances, typically between 100 meters and 1,000 meters, and operate at power levels substantially below those of macrocells.
Mid-block lane – See Street/Road-Related Definitions.
Middle housing – Means a category of housing types that includes duplexes, triplexes, fourplexes, single-family attached dwellings, and cottage clusters.
Ministerial – See Land Use Decision Types.
Mitigation – To avoid, rectify, repair, or compensate for negative impacts which result from other actions (e.g., improvements to a street may be required to mitigate for transportation impacts resulting from development).
Mixed-use building/development – Includes a variety of complementary uses – including but not limited to residential, service, office, retail and civic uses – that are integrated vertically or horizontally within a single building or multiple buildings on a lot or development site.
Moderate visibility means the following facilities if they do not exceed the height limit of the applicable zoning district, or do not increase the height of an existing facility, unless approved through a Conditional Use Permit:
1. Panel-shaped antennas not exceeding eight feet in length or height that are flush-mounted to an existing building facade or other existing structure on at least one edge, or extend a maximum of 24 inches from the building facade or other structure at any edge, do not exceed the height of the building or other structure, and are designed to blend with the color, texture, and design of the existing building or structure, with equipment cabinets that are screened from view.
2. Wireless or broadcast communication facilities that are camouflaged, such as faux trees, flag poles, and light poles; provided, that the equipment building, shelter, or cabinet for the facility is screened or camouflaged.
Monopole means a wireless or broadcast communication facility consisting of a single pole constructed for purposes of supporting one or more antennas without guy wires or ground anchors.
Multi-family development – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Multi-use path – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Multi-use trail – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Municipal Code – Means the Sisters Municipal Code as the same may be amended from time to time.
N
Natural hazard – Natural areas that can cause dangerous or difficult development situations. For example, natural hazard areas may include steep slopes, unstable soils, landslides, or areas subject to flooding.
Natural open space – See Open Space Definitions.
Neighborhood character means those unique attributes including, but not limited to, architecture, historical and cultural features, historical development patterns, landscape, hardscape, and the size, scale and spacing of buildings and other structures that define a neighborhood’s identity.
Neighborhood Market – A small grocery store, 6,000 square feet or smaller.
Neighborhood-scale design – Site and building design elements that are dimensionally related to housing and pedestrians, such as narrower streets with tree canopies, smaller parking areas, lower building heights (as compared to downtown areas) and similar neighborhood characteristics.
Non-conforming use/non-conforming development – An existing land use/structure that would not be permitted by the regulations imposed by the current Development Code, but was lawful at the time it was established.
Nude/Nudity – Being devoid of a covering for the male or female genitalia consisting of an opaque material which does not simulate the organ covered, and in the case of a female, exposing to view one or both breasts without a circular covering, centered on the nipple, that is at least 3 inches in diameter and does not simulate the organ covered.
O
Off-street parking – All off-street areas designed, used, required or intended to be used for the parking of motor vehicles. Parking areas do not include driveways or drive aisles.
On-street parking – Parking in the street right-of-way, typically in parking lanes or bays. Parking may be “parallel” or “angled” in relation to the edge of the right-of-way or curb.
Open space definitions:
|
• |
Developed open space – includes enhanced or developed landscape set aside as a common area for the purpose of active or passive recreation. Developed open space requires improvements to support and promote higher levels of public use. Improvements may be publicly or privately owned and/or maintained and may include, but are not limited to irrigated and maintained landscaped areas, open play areas and fields, golf courses, playgrounds, picnic shelters and seating, trails or pathways, community plazas. Developed open space does not include landscaped areas or planter strips within a public right-of-way. |
|
• |
Natural open space – natural, undisturbed landscape set aside (through dedication, conservation easement or an open space tract) for the purpose of preservation or conservation of natural resources, natural features or scenic/aesthetic values. |
|
• |
Private open space – includes private yards, balconies, porches and other outdoor areas that may be landscaped but that are not generally available for public access or use. |
Opposite – Placed or located directly across from something else or from each other.
Oriel window – Similar in style and function to a bay window but that project out beyond or is not supported flush by the building foundation.
Outdoor commercial use – A use supporting a commercial activity which provides goods or services, either wholesale or retail, where the amount of site area used for outdoor storage of materials or display of merchandise exceeds the total floor area of all buildings on the site. Examples of outdoor commercial uses include automobile sales or services, nurseries, lumber yards and equipment rental businesses.
Overlay zone/district – A supplemental zoning designation for a property or area that may provide more restrictive regulations than the underlying zoning designation.
P
Panel or directional antenna means an antenna or array of antennas designed to concentrate a radio signal in a particular area.
Parcel – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Park – Public or privately owned land set apart and devoted to the purposes of pleasure, recreation, ornament, light and air for the general public. Parks may include picnic areas, playgrounds, indoor recreation facilities, athletic fields, courts, amphitheatres and open space.
Parking Area – Privately or publicly owned property other than streets or alleys, on which parking spaces are defined, designated or otherwise.
Partition – To divide land to create not more than three parcels of land within a calendar year. See also ORS Chapter 92.
Pathway – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Pedestrian facilities – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Pedestrian-oriented development – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Personal wireless service facility for small wireless facilities means an antenna facility or a structure that is used for the provision of personal wireless service, whether such service is provided on a stand-alone basis or commingled with other wireless communications services.
Pier – Exterior vertical building elements that frame each side of a building or its ground-floor windows (usually decorative).
Planter strip – A landscape area for street trees and other plantings within the public right-of-way or other area intended for public use, usually between the street and a sidewalk.
Plat, Final – The final plan of all or a portion of a subdivision or partition that is presented to the approving authority for final signature and recording in accordance with state law.
Plat, Tentative – A plan of all or a portion of a subdivision or partition that is submitted for approval in accordance with state law, and that is not a final plat.
Plaza – A public square or extra-wide sidewalk (e.g., as on a street corner) that allows for special events, outdoor seating, sidewalk sales, and similar pedestrian activity.
Pocket park – A small park, usually less than one-half acre in size.
Porch – A covered exterior area attached to a structure or dwelling; six (6) feet or greater in depth.
Primary – The largest or most substantial of a given element on the property. This may include the use, residence, entrance, etc. All other similar items are secondary in size or importance.
Private open space – See Open Space Definitions.
Public art – Including but not limited to, paintings, sculptures, site specific installations, engravings, carvings, frescos, mobiles, murals, collages, mosaics, statues and bas-reliefs. However, the following shall not be considered “public art ”:
(1) Art objects which are mass produced;
(2) Works that are decorative, ornamental or functional elements of the architecture or landscape design, except when commissioned from an artist as an integral aspect of a structure or site;
(3) Architectural rehabilitation or historical preservation.
Public works construction standards or public works standards and specifications – Standards and specifications for public improvements, infrastructure (including without limitation streets, water, and sewer facilities), and construction within public rights-of-way, public utility easements, and other public property promulgated by the City as may be amended from time to time.
Q
Quasi-judicial – See Land Use Decision Types.
R
Rear lot line – See Lot Line Definitions.
Recreation Area, Indoor – A room or rooms within an enclosed building which is designed and used for recreational purposes by the public and/or occupants of a residential development. Activities provided for within an indoor recreation area may include, but are not limited to, the following: indoor swimming pools, saunas, gymnasiums, exercising rooms, dance, music or martial art studios, tennis or handball courts, and games such as pool, ping- pong, shuffleboard, etc.
Recreational facility, private means a recreation facility under private ownership and operated by a for profit or nonprofit organization, open to members, and providing one or more of the following types of recreation activity, fitness center, indoor gymnasium, spa or health center including: tennis, handball, golf, squash, volleyball, racquetball, badminton, skate park and swimming.
Recreational facilities, public means a publicly-owned facility, land, or improvements designated for leisure and recreational activities, open to the general public, with or without payment of fees.
Recreational vehicle – A vehicular type portable structure without permanent foundation, which can be towed, hauled or driven and primarily designed as temporary living accommodation for recreational, camping and travel use and including but not limited to travel trailers, truck campers, camping trailers and self-propelled motor homes.
Recreational vehicle park – Two or more recreational vehicles located on one lot and as permitted by the underlying zoning district.
Residential care – Services such as supervision; protection; assistance while bathing, dressing, grooming or eating; management of money; transportation; recreation; and the providing of room and board.
Residential care facility – A facility that provides, for six or more socially dependent individuals or individuals with physical disabilities, residential care in one or more buildings on contiguous properties.
Residential facility – A residential care facility, residential training facility, residential treatment facility, residential training home or residential treatment home.
Residential home – A residential treatment or training or adult foster home licensed by or under the authority of the department, as defined in ORS 443.400, under ORS 443.400 to 443.825, a residential facility registered under ORS 443.480 to 443.500 or an adult foster home licensed under ORS 443.705 to 443.825 that provides residential care alone or in conjunction with treatment or training or a combination thereof for five or fewer individuals who need not be related. Staff persons required to meet licensing requirements shall not be counted in the number of facility residents, and need not be related to each other or to any resident of the residential home.
Retail Sales Establishment – An establishment or place of business primarily engaged in selling goods directly to the consumer, where such goods are generally available for immediate purchase and removal from the premises by the purchaser.
RF means radio frequency.
Ridge line – See Building-Related Definitions.
Right-of-way – Land that is owned in fee simple by the public, usually for transportation facilities, or in an easement.
Roof pitch – See Building-Related Definitions.
Roof-top garden – A garden on a building terrace, or on top of a building with a flat roof (usually on a portion of a roof).
S
Screened means concealed from view with a sight-obscuring fence, wall or vegetation.
Senior housing – Housing designated and/or managed for persons over the age of 55. (Specific age restrictions may vary.)
Sensitive lands – Wetlands, significant trees, steep slopes, flood plains and other natural resource areas designated for protection or conservation by the Comprehensive Plan or other state and federal agencies.
Series partition – The creation of more than three lots in more than one calendar year from one parent parcel through a partition process. Subdivision standards and requirements may be applied to a series partition. Note: the creation of more than 3 lots within one calendar year is a subdivision.
Service area means the area served by a single wireless or broadcast communication facility.
Service Station – A vehicle fueling station that also may offer such services as oil change and minor mechanical repairs to automobiles in an enclosed area and may include a convenience market.
Setback – Yard setbacks are measured along a horizontal plane from a property line to the edge of a building wall, or structure as defined herein. Minimum and maximum setbacks may be required from front, side and rear property lines.
Shared driveway – Common street access used by two or more lots or parcels. An easement or tract (owned in common) may be created for this purpose.
Shared parking – Required parking facilities for two or more uses, structures, or parcels of land that may be satisfied by the same parking facilities used jointly, to the extent that the owners or operators show that the need for parking facilities does not materially overlap.
Shooting Range – An enclosed firing range with targets for rifle or handgun practice. Shooting gallery.
Short-term rental permit – An approved development application authorizing a short-term rental.
Short-term rental(s) – The use of a dwelling unit (or a habitable portion of a dwelling unit) by any person or group of persons entitled to occupy the dwelling unit for rent for a period of less than thirty (30) consecutive days. Short-term rental(s) also means a vacation home rental approved under the regulations in effect through December 27, 2018, and owner-occupied short-term rentals. “Short-term rental(s)” does not mean bed and breakfast inns, hotels, and/or motels.
Shoulder bikeway – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Side lot line – See Lot Line Definitions.
Sidewalk – See Bicycle/Pedestrian Related Definitions.
Significant Trees – Individual trees with a trunk diameter of eight (8) inches or greater as measured 4.5 feet above the ground (DBH), shall be identified as significant.
Single-family attached dwelling (townhome) – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Single-family detached dwelling – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Single-family detached “Zero Lot Line” Dwelling – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Site – A property (or group of adjacent parcels or lots under the same ownership) that is subject to a permit application under this Code.
Site Plan Review – Site Plan Review ensures compliance with the basic development standards of the land use district, as well as the more detailed design standards and public improvement requirements in Chapters 2 and 3.
Small top-mounted antennas means any antenna mounted on the top of a tower structure where the antenna is 20 feet or less in height and six inches or less in outside diameter.
Small wireless facility means a low-power wireless communication facility used to increase capacity to wireless communication demand areas or provide infill coverage in areas of weak reception, including a separate transmitting and receiving station serving the facility, or anything that is considered a small wireless facility under Federal law.
Specific Area Plan – Describes in more detail the type of development planned for a specific area than is typically found in a comprehensive plan, zone map, or public facilities plan.
Standards – Standards are code requirements.
Stealth means facilities, including, but not limited to, microcells, antennas, equipment cabinets, and any other ancillary equipment, that cannot be seen from any street or any adjacent property, improved or unimproved, and that do not result in any apparent architectural changes or additions to existing buildings. The addition of landscaping, walls, fences, or grading as screening techniques does not make an otherwise visible facility a stealth facility.
Steep slopes – Slopes that are greater than 20 percent.
Storefront character – The character of a commercial building expressed by buildings with ground-floor display windows, weather protection (e.g., awnings or canopies), corner building entrances or recessed entries, and similar features.
Stormwater facility – A facility designed to improve the quality and manage the quantity of stormwater runoff. Stormwater facilities include vegetated swales and sand filters, wet or dry ponds, marshes, infiltration facilities, and structural storm sewer devices. Stormwater facilities do not include conveyance systems that are meant only for conveying the stormwater from one place to another and do not affect the quality or quantity of the stormwater.
Street/Road-Related Definitions:
|
• |
Alley – A narrow way providing a means of public or private access to the back or side of a property and not intended for general traffic circulation. |
|
• |
Arterial street – Arterial streets serve to interconnect the City. These streets link major commercial, residential, industrial and institutional areas. Arterial streets reduce the incidence of traffic using collectors or local streets for through traffic in lieu of a well placed arterial street. Access control is the key feature of an arterial route. |
|
• |
Collector street – Collector streets provide both access and circulation within and between residential and commercial/industrial areas. Collectors differ from arterials in that they provide more of a citywide circulation function, do not require as extensive control of access (compared to arterials) and penetrate residential neighborhoods, distributing trips from the neighborhood and local street system. |
|
• |
Frontage street – A designated local street that parallels an arterial street in order to provide access to abutting properties and minimize direct access onto the arterial. |
|
• |
Hammerhead turn-around – A “T” or “L” shaped dead-end street that allows for vehicles to turn around. |
|
• |
Local street – Local streets have the sole function of providing immediate access to adjacent land. Service to through traffic movements on local streets is deliberately discouraged by design. All other city streets in the City of Sisters that are not designated as arterial streets, collector streets, or neighborhood routes are considered to be local streets. |
|
• |
Mid-block lane – A narrow, limited use roadway facility usually used to access a limited number of dwelling units, similar to an alley in design. |
|
• |
Neighborhood Routes – Neighborhood routes are usually long relative to local streets and provide connectivity to collectors or arterials. Because neighborhood routes have greater connectivity, they generally have more traffic than local streets and are used by residents in the area to get into and out of the neighborhood, but do not serve citywide/large area circulation. |
|
• |
Street/Road – A public or private thoroughfare or right-of-way dedicated, deeded or condemned for use as such, which affords access to two or more parcels of abutting property. |
|
• |
Street stub – A temporary street ending where the street will be extended through adjacent property in the future, as those properties develop. Not a permanent street-end or dead-end street. |
Street connectivity – The number and distance of street connections to other streets within a specific geographic area.
Street furniture/furnishings – Benches, lighting, bicycle racks, drinking fountains, mailboxes, kiosks, and similar bicycle and pedestrian amenities located within a public right-of-way.
Street stub – See Street/Road-Related Definitions.
Street tree – Any tree located within the public or private right of way or easement for vehicular access, or associated public utility easements.
Structure – Any object constructed in or on the ground. Structure includes buildings, decks, fences, towers, flag poles, signs, and other similar objects. Structure does not include uncovered paved areas or vegetative landscaping materials.
Studio, artist – An artist’s or worker’s workroom, or an artist and his or her employees who work within that studio. This can be for the purpose of architecture, painting, pottery (ceramics), sculpture, photography or animation.
Subdivision – To divide land to create four or more lots within a calendar year. See also ORS Chapter 92.
Swale – A broad, shallow depression designed for storm water runoff channelization, which might contain plants to filter contaminants.
T
Tandem Parking – Residential motor vehicle parking where two motor vehicles park nose-to-end in tandem. The first motor vehicle does not have independent access, and the second motor vehicle must move to provide access.
Telecommunications means the transmission, between or among points specified by the user, of information of the user’s choosing, without change in the form or content of the information as sent and received.
Temporary Use – A short-term, seasonal, or intermittent use. A temporary use is one established for a fixed period of time with the intent to discontinue such use upon the expiration of such time. Such uses do not involve the construction or alteration of any permanent structure.
Terrace – A landing or promenade supported by columns, or a flat roof or other platform on a building.
Theater – A building, room, or outdoor structure for the presentation of plays, films, or other dramatic performances.
Through lot – See Lot-Related Definitions.
Topographic constraint – Where existing slopes or other (non-vegetative features) prevent conformance with a Code standard.
Tower or telecommunications tower means any mast, pole, monopole, guyed tower, lattice tower, freestanding tower, or other structure designed and primarily used to support antennas.
Townhome – See Dwelling-Related Definitions.
Tract: private/public – A piece of land set aside in a separate area for dedication to the public, a homeowner’s association, or other entity (e.g., open space tract for open space, recreation facilities, sensitive lands, etc.); or, a tract can define a land area reserved for future development.
Transportation facilities and improvements – The physical improvements used to move people and goods from one place to another; i.e., streets, sidewalks, pathways, bike lanes, airports, transit stations and bus stops, etc. Transportation improvements include the following:
a. Installation of culverts, pathways, medians, fencing, guardrails, lighting, and similar types of improvements within the existing right-of-way.
b. Projects specifically identified in the City’s adopted Transportation System Plan as not requiring further land use review and approval.
c. Landscaping as part of a transportation facility.
d. Emergency measures necessary for the safety and protection of property.
e. Construction of a street or road as designated in the City’s adopted Transportation System Plan, except for those that are located in exclusive farm use or forest zones.
f. Construction of a street or road as part of a subdivision or land partition.
Transportation mode – The method or transportation (e.g., automobile, bus, walking, bicycling, etc.)
Triplex – See Dwelling Related Definitions.
U
Urban Forestry:
|
• |
City Property – Real property owned or controlled by the City either within or outside the City limits. |
|
• |
Crown – The leaves and branches of a tree measured from the lowest branch on the trunk to the top of the tree. |
|
• |
Hazardous Tree – A tree or tree part that has a high potential to fail and cause damage or injury to people or property. |
|
• |
Major Prune – The selective removal of 20% or more of a tree’s crown. |
|
• |
Pruning – The selective cutting and removal of plant parts to meet specific goals and objectives. |
|
• |
Public Tree – Any tree located on City of Sisters property or in a public right-of-way over which the City of Sisters has jurisdiction. |
|
• |
Topping – An inappropriate technique to reduce tree size; cutting a stem more than 2 years old at an indiscriminate location or back to a lateral branch too small to keep the cut stem vital (typically less than 1/3 the diameter of the cut stem); a type of pruning cut that destroys tree architecture and serves to initiate discoloration and perhaps decay in the cut stem. |
|
• |
Tree – A woody perennial, usually with one main trunk, that is or will attain a height of at least six feet or a trunk diameter of at least 2 inches at 4.5 feet above natural grade. |
|
• |
Urban Forest Management Plan – A document that guides the work of the City’s urban forestry program and envisions a long range plan for the preservation and improvement of the Sisters urban forest. The Plan shall provide a 10-year outline for achieving urban forestry administrative, policy, educational and management goals and may contain such data as deemed necessary by the Planning Director or designee, with advice from the City Urban Forestry Board, to carry out its legal mandate. This Plan will further implement the policies and goals of the City of Sisters Comprehensive Plan. The initial Plan and subsequent updates are subject to the approval of the City Council. |
|
• |
Urban Forestry – The planting, management and maintenance of trees and related vegetation growing within the city’s urban growth boundary for the present and potential positive benefits and contributions to the health and livability of the city. |
Utilities – Public or private infrastructure which includes but is not limited to sewer, water, electric, telephone, natural gas and cable television.
Utility Facility – Any major structure owned or operated by a public, private or cooperative electric, fuel, communication, sewage or water company for the generation, transmission, distribution or processing its products or for the disposal of cooling water, waste, or by-products, and including power transmission lines, major trunk pipelines, power substations, dams, water towers, sewage lagoons, sanitary landfills and similar facilities, but excluding sewer, water, gas, telephone and power local distribution lines and similar minor facilities allowed in any zone.
V
Vacate plat/street – To abandon a subdivision or street right-of-way. A plat may be vacated, returning the property to an undivided condition. A public right-of-way that is not needed or cannot be used for a street or other public purpose may also be vacated, subject to statutory requirements.
Vacation rental – See Short-Term Rental Definition.
Variance – An administrative or quasi-judicial decision to lessen or otherwise modify the requirements of this Code.
Veterinary animal clinic – A place where animals or pets are given medical or surgical treatment and are cared for during the time of such treatment. Use as a kennel shall be limited to short-time boarding and shall be only incidental to such hospital use.
Vision clearance area – A triangular three-dimensional space located at the intersection of a street (public or private) and a driveway, alley, lane, or other vehicle way that is not a street or at an intersection of two streets (public or private) having 90 degree angles at the intersection, established to protect the visibility of pedestrians, cyclists and persons in motor vehicles.
Vocational School – A use providing post secondary education or training in business, technology, commercial trades, language, arts or other similar activity or occupational pursuit.
W
Wetland – Wetlands are land areas where water is the dominant factor determining the nature of soil development and the types of plant and animal communities. Wetlands are defined more specifically by the Federal Clean Water Act (Section 404) and Oregon Administrative Rules (OAR 141-85-010).
Whip antenna means an antenna that transmits or receives signals in 360 degrees. Whip antennas are typically cylindrical in shape, less than three inches in diameter and no more than six feet long, including the mounting.
Window hood – An architectural detail placed above a window, used as an accent.
Wireless communication facility means any facility that transmits and/or receives electromagnetic waves, including, but not limited to, antennas, dish antennas, microwave antennas, and other types of equipment for the transmission or receipt of such signals, including telecommunications towers and similar supporting structures, equipment cabinets or buildings, parking areas, and other accessory development. This definition does not apply to amateur radio stations as defined by the Federal Communications Commission, Part 97 of the Commission’s Rules.
Workforce housing unit – Housing reserved for occupancy by eligible households and affordable to households whose annual income does not exceed 150 percent of area median income, adjusted for household size, and no more than 30 percent of the monthly household income is paid for monthly housing expenses. (Housing expenses for ownership housing include mortgage and mortgage insurance, property taxes, property insurance, and homeowner dues. Housing expenses for rental housing include rent and appropriate utility allowance.)
Y
Yard – The area between buildings and property lines generally defined by setbacks.
Z
Zero-lot line dwelling – See Dwelling-Related Definitions. [Ord. 533 § 3 (Exh. C), 2023; Ord. 528 § 4 (Exh. G), 2023; Ord. 526 § 3 (Exh. B), 2022; Ord. 505 § 2 (Exhs. C, D), 2020; Ord. 497 § 2 (Exh. B), 2019; Ord. 489 § 2 (Exh. B), 2018; Ord. 486 § 2 (Exh. B), 2018; Ord. 478 § 1 (Exh. A), 2017].